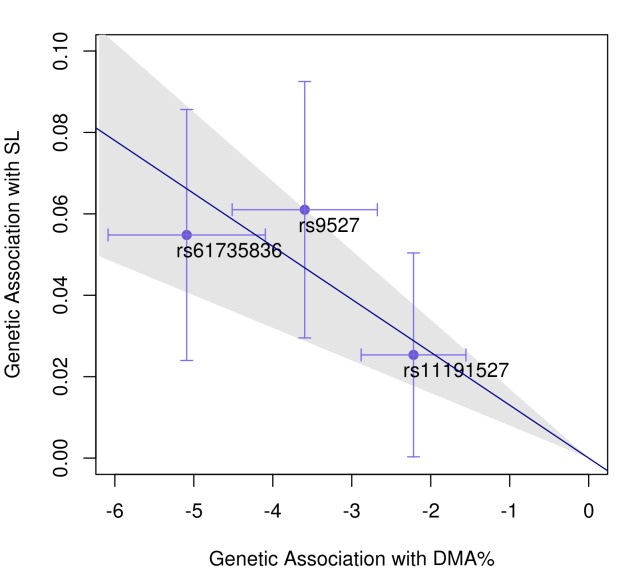
Fig 5. Mendelian randomization supports a causal effect of arsenic metabolism efficiency on arsenic-induced skin lesion risk.
Horizontal and vertical error bars for each SNP correspond to the 95% CI for the beta coefficient for its association with DMA% and skin lesion risk, respectively. The slope of the diagonal line (-0.013) is the inverse-variance-weighted estimate of the causal effect (i.e., the ln(OR), corresponding to OR = 0.89 for a 10% increase in DMA%; P = 6x10-8).