-
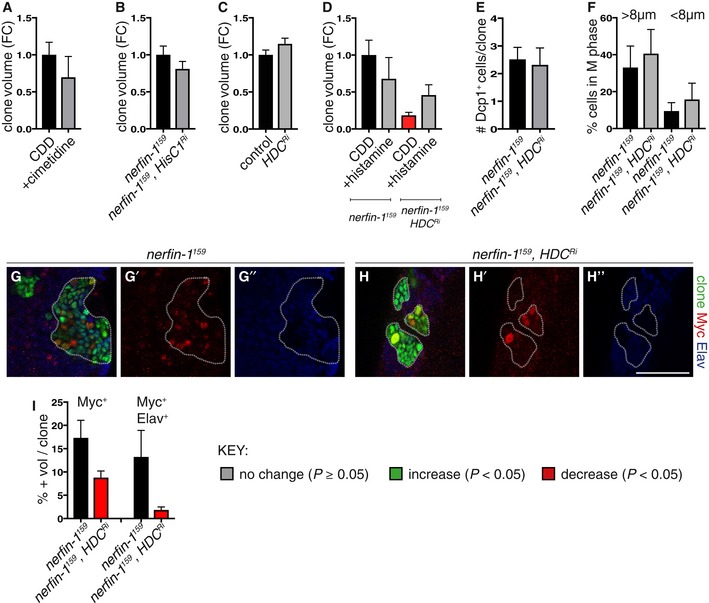
A
500 mg/ml of the histamine receptor inhibitor cimetidine (n = 39, 23) did not significantly alter nerfin‐1 clonal growth in the adult CNS.
-
B
Knockdown of histamine inhibitor HisCl1 (HisCl1
Ri), knockdown verified in Oh
et al,
2013, did not significantly alter
nerfin‐1 clonal growth in the larval CNS (
n = 37, 42).
-
C
Hdc knockdown did not significantly alter the growth of wildtype larval CNS clones (n = 42, 36).
-
D
Histamine supplementation did not significantly increase nerfin‐1 clone size, but significantly rescued nerfin‐1;HdcRi clonal growth in the larval CNS (n = 15, 10, 12, 9).
-
E
Hdc knockdown did not significantly alter the amount of cell death in nerfin‐1 clones in the larvae (n = 43, 35).
-
F
The speed of the cell cycle in fully dedifferentiated NBs > 8 μm (n = 11, 9) and dedifferentiating neurons < 8 μm (n = 11, 9) was not significantly altered by Hdc inhibition in nerfin‐1 larval clones.
-
G–I
Representative pictures showing that Hdc inhibition significantly reduced the % of Myc+ NBs (red) and Myc+ Elav+ (blue) neurons in nerfin‐1 larval clones (G–H’’), quantified in (I) (n = 14, 14, 13, 16). Scale bar = 50 μm.
Data information: In all graphs, the key indicates that green bars represent a significant increase (
P < 0.05), red bars a significant decrease (
P < 0.05), and grey bars no significant change (
P > 0.05) in
t‐tests with the relevant paired controls (black bar). In all graphs, error bars represent 1 standard error of the mean (SEM). FC, fold change.