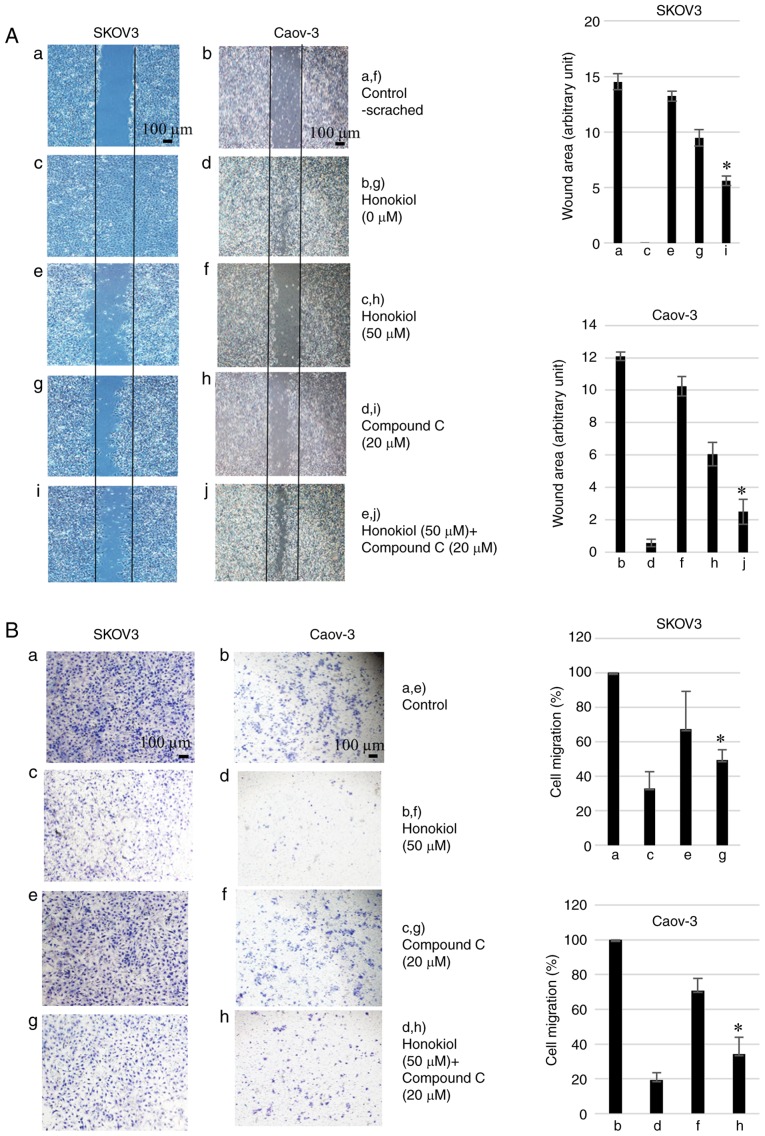
Figure 4.
Honokiol inhibits ovarian cancer cell migration and invasion. (A) Cells were cultured until a monolayer was formed, which was then scratched with a pipette tip. Images of wounds at 0 h were captured. After 48 h (SKOV3) or 72 h (Caov-3) incubation, plates were observed with a phase-contrast microscope at magnification, ×40. The area without cells was measured by ImageJ software in arbitrary units. Results are representative of three independent experiments. (A-a) Control treatment in SKOV3 cells at 0 h. (A-b) Control treatment in the Caov-3 cells at 0 h. (A-c) Honokiol treatment (0 µM) in SKOV3 cells at 48 h. (A-d) Honokiol treatment (0 µM) in Caov-3 cells at 72 h. (A-e) Honokiol (50 µM) treatment in SKOV3 cells at 48 h. (A-f) Honokiol (50 µM) treatment in Caov-3 cells at 72 h. (A-g) Compound C (20 µM) treatment in SKOV3 cells at 48 h. (A-h) Compound C (20 µM) treatment in Caov-3 cells at 72 h. (A-i) Honokiol (50 µM) + Compound C (20 µM) treatment in SKOV3 cells at 48 h. (A-j) Honokiol (50 µM) + Compound C (20 µM) treatment in Caov-3 cells at 72 h. *P<0.05 vs. honokiol-only treatment (e and f). Scale bars, 100 µm. (B) Cells treated with honokiol (50 µM) and/or compound C (20 µM) were plated onto the upper part of the Matrigel invasion chamber. After 48 h (SKOV3) or 72 h (Caov-3) incubation, invasive cells that had migrated to the lower part of the membrane were stained with trypan blue and observed using a phase-contrast microscope at magnification, ×40. (B-a) Control treatment in SKOV3 cells. (B-b) Control treatment in the Caov-3 cells. (B-c) Honokiol treatment (50 µM) in SKOV3 cells. (B-d) Honokiol treatment (50 µM) in Caov-3 cells. (B-e) Compound C (20 µM) treatment in SKOV3 cells. (B-f) Compound C (20 µM) treatment in Caov-3 cells. (B-g) Honokiol (50 µM) + Compound C (20 µM) treatment in SKOV3 cells. (B-h) Honokiol (50 µM) + Compound C (20 µM) treatment in Caov-3 cells. *P<0.05 vs. honokiol-only treatment (c and d). Scale bars, 100 µm.