Figure 3. Regulation of Smo trafficking and conformation.
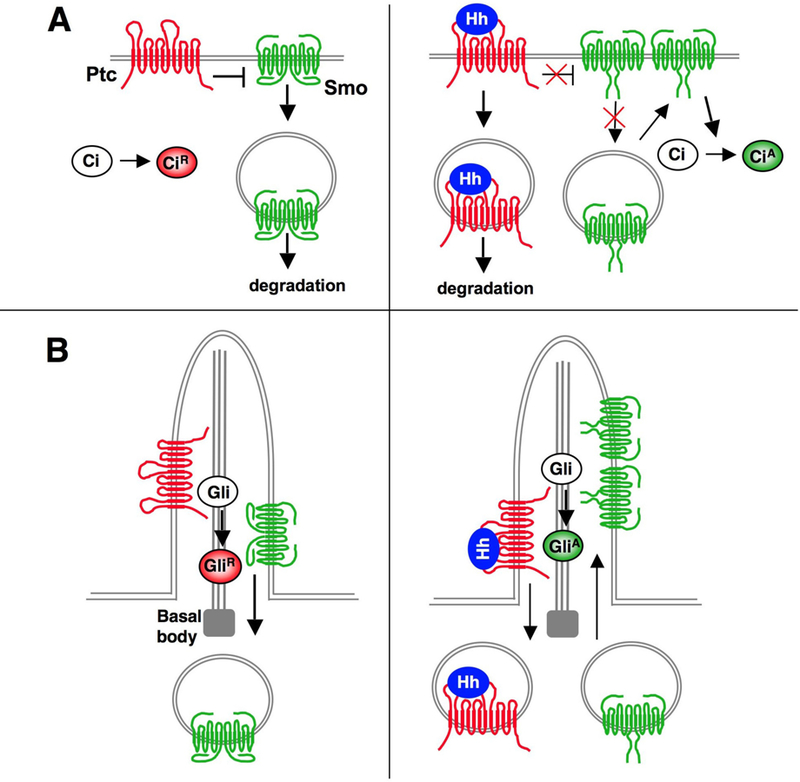
(A) In Drosophila, the absence of Hh allows Ptc to inhibit Smo phosphorylation, which promotes Smo endocytosis and degradation. Binding of Hh to Ptc stimulates Smo hyperphosphorylation, which increases Smo cell surface expression by inhibiting endocytosis and/or promoting recycling. In addition, phosphorylation of Smo promotes a conformational change leading to oligomerization of Smo C-tails
(B) In mammals, Ptc resides in the primary cilium and prevents Smo ciliary accumulation in the absence of Hh. Hh binding to Ptc promotes the exit of Ptc from the cilium and allows Smo to accumulate in the cilium. Hh also induces conformational change and clustering of Smo C-tails.
