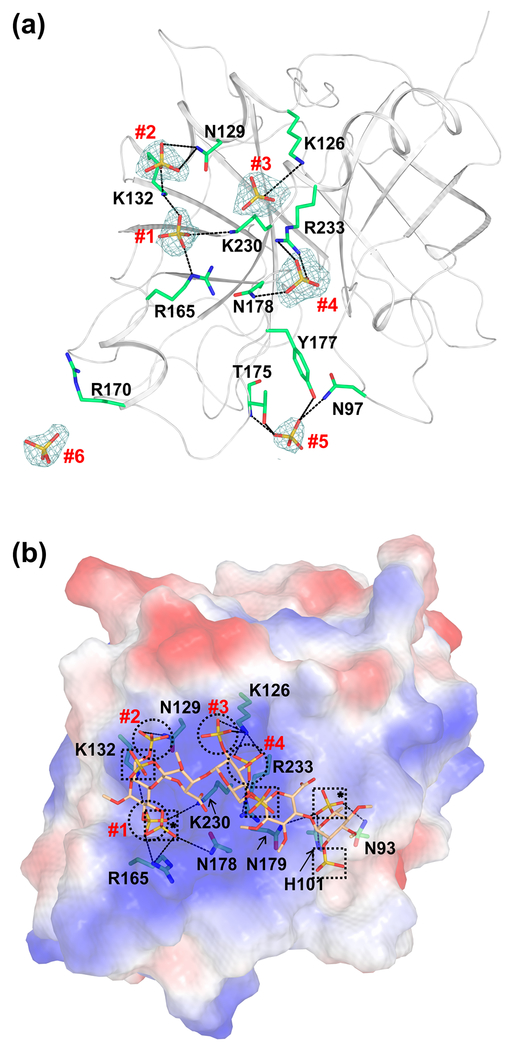
Fig. 5. Cartoon and electrostatic surface representations of the FIXa protease domain containing the sulfate ions and the modeled heparin binding mode.
(a) The sulfate ions found in the FIXa protease domain crystal structure. The sulfate ions and the side chain of residues involved in the salt-bridge and hydrogen bond interactions are shown in stick representation. The electron density (2Fobs−Fcalc) only of the sulfate ions (numbered #1 to #6) contoured at 1σ is shown. Densities are carved to 1.7 Å around the sulfate ions. (b) Mode of heparin binding to the FIXa protease domain. Electrostatic surface potential of the FIXa protease domain is shown with heparin fragment in stick representation. The FIXa heparin binding mode was modeled using the structure of thrombin bound to the heparin fragment [49]. Sulfates from the heparin fragment that occupy the same positions (#1 to #4) as the sulfates found in the crystal structure of FIXa are represented by circles. The other sulfates from the heparin fragment are marked with squares and those involved in interactions with FIXa are marked with asterisks. The salt-bridge interactions between FIXa residues and the sulfates in heparin are shown in dashed lines. Sulfates #5 and #6 of panel (a) do not match with any of the sulfates from the heparin fragment and thus are not depicted here.