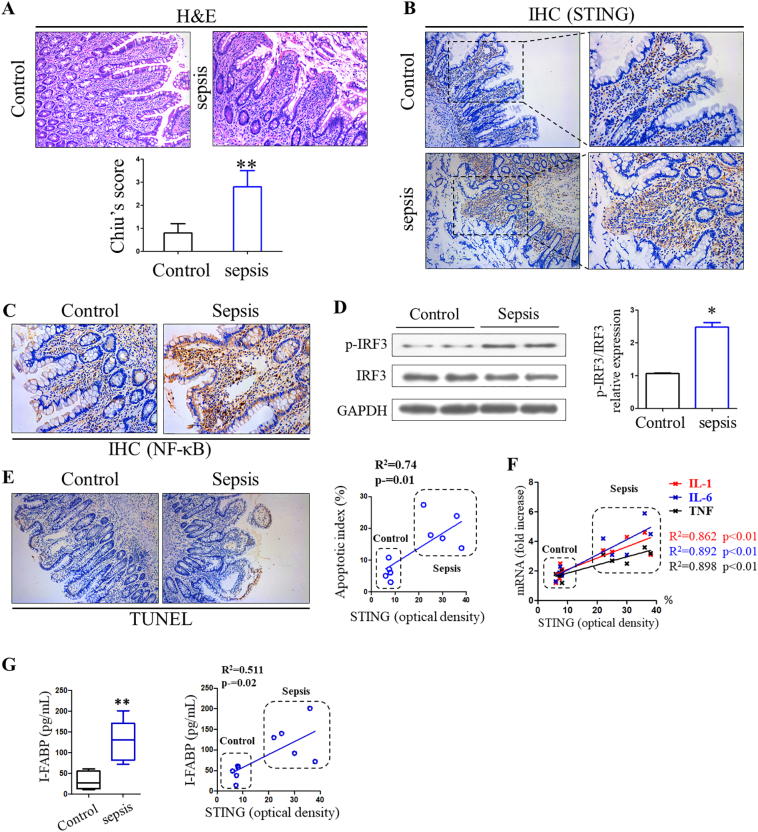
Fig. 1.
Stimulator of interferon genes (STINGs) was activated in sepsis and correlates with intestinal inflammation and gut barrier dysfunction. (A) Representative images of intestinal histology (H&E staining) in control group and sepsis patients. (B) Expression level of STING and (C) NF-κB in human intestines were analyzed through IHC staining. (D) Activation of IRF3 signaling in gut of sepsis patients. (E) Correlation between apoptosis indexes and expression of STING in human gut. (F, G) Correlation of inflammatory cytokines and I-FABP to the expression level of STING. Image J was used to detect STING optical density, and each symbol represents an individual patient. H&E, hematoxylin and eosin; IHC, immunohistochemistry, IRF3, interferon regulatory factor 3; I-FABP, intestinal fatty acid binding protein. ⁎P < .05, ⁎⁎P < .01 vs control group.