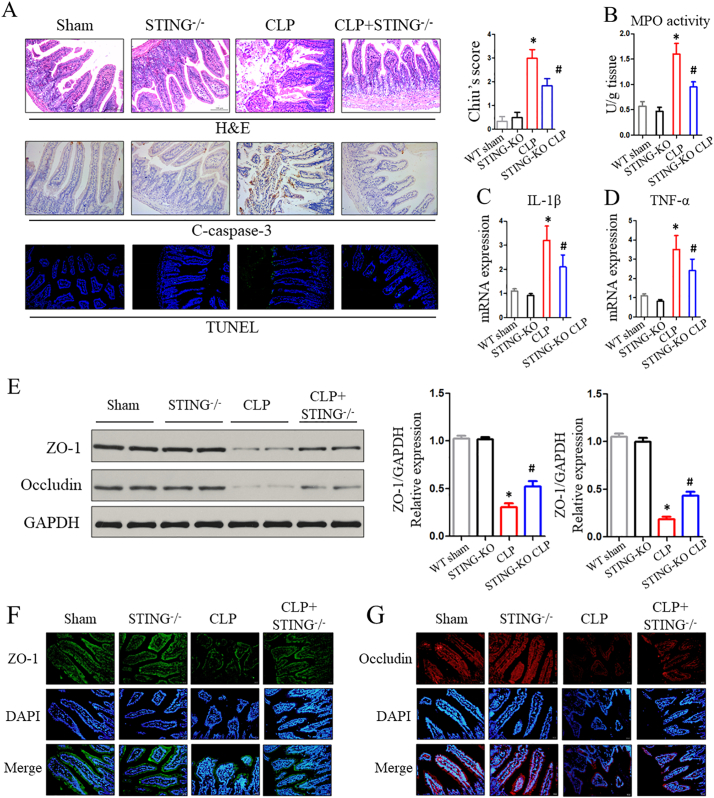
Fig. 4.
Inhibition of the STING signaling protects against CLP-induced intestinal injury. (A) Representative images of H&E, c-caspase3, and TUNEL staining in WT and STING-KO mice after CLP treatment. (B, C, D) MPO activity and inflammatory cytokines within intestinal mucosa. (E) Proteins levels of ZO-1 and occludin in intestinal tissue were assessed by western blot. (F, G) Localization of ZO-1 and occludin within intestinal mucosa evaluated by immunofluorescence after CLP. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD. ⁎P < .05 vs sham group; #P < .05 vs CLP group. n = 6 mice per group.