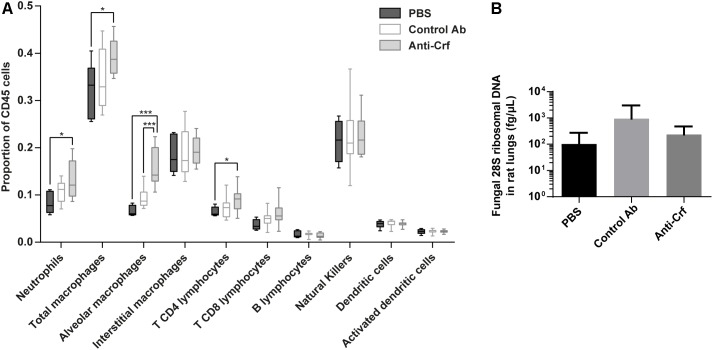
FIGURE 6.
Anti-Crf IgG1 antibody effects in a rat model of IPA. Neutropenic rats were infected by 105 spores of Crf+ strain, and challenged extemporaneously either with intra-tracheal aerosolization of PBS (n = 6), control antibody (Control Ab, n = 12) or anti-Crf IgG1 antibody (n = 12). Antibody were administered twice (4 mg/kg), with the spores and 32 h post-infection. Rats were sacrificed 72 h after the infection. (A) Evaluation of IgG1 effects on the recruitment of immune cells on infected rat lungs. Immune cells were extracted from lungs and processed in flow cytometry. Neutrophils (CD11bhi, Ly6Ghi), total macrophages (CD11bhi, Ly6Glow), alveolar macrophages (CD11bhi, Ly6Glow, CD172hi, CD68hi), interstitial macrophages (CD11bhi, Ly6Glow, CD172low, CD68hi), T CD4 lymphocytes (CD4+, TCR+), T CD8 lymphocytes (CD8a+, TCR+), B lymphocytes (CD45R+, IgM+), natural killers (KLRB1+), dendritic cells (CD11chi, MHC-IIhi) and activated dendritic cells (CD11chi, MHC-IIhi, CD86hi) populations were studied. Results are expressed in median ± interquartile (box) with min/max (bars); Mann–Whitney statistical test was used. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗∗p < 0.001. (B) Evaluation of IgG1 effects on the lung fungal load of a rat model of IPA. Fungal DNA was extracted from lungs and A. fumigatus load was assessed by assaying 28S ribosomal DNA by qPCR. Results are expressed in mean ± SD; Mann–Whitney statistical test was used.