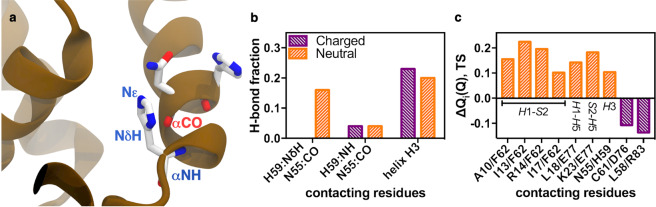
Figure 5.
Hydrogen bond and contact probability changes due to protonation of H59 in MD simulations. (a) Structural representation of helix H3, depicting H59 and N55 interaction, and showing the side chain nitrogen atoms (δ and ε) of the H59 around carbonyl group (CO) of N55. (b) Side chain backbone and backbone-backbone hydrogen bond quantifications between charged (purple) or neutral (orange) H59 and N55 from helix H3, as well as total hydrogen bonds for helix H3. (c) Differences in contact probability on the folding TS for monomeric FoxP1 between residues from helices H1, H3 and H5 and strand S2. Changes towards higher contact probability for the deprotonated H59 are shown in orange, whereas changes favouring the protonated state are shown in purple.