Figure 3.
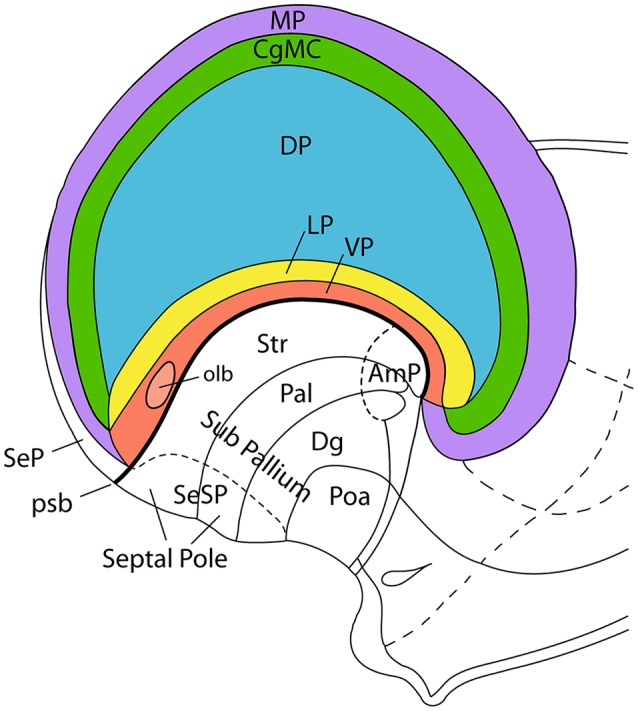
Incipient axial bending in the mammalian telencephalon, divided into pallial regions. This schema represents the pallial bauplan showing medial (MP; violet), dorsal (DP; blue), lateral (LP; yellow), and ventral (VP; red) pallial regions. The cingulate mesocortex (CgMC; green) is included as well, so that MP and VP form the external allopallial ring, while CgMC and LP form the transitional mesopallial ring that encloses the central DP island. The schema shows how the flat pallial map shown in Figure 1 can be visualized in a lateral view at an embryonic stage in which the septal and amygdalar poles of the hemisphere (Septal Pole; AmP) start to be pushed downwards by differential growth of the DP (isocortex). This incipient deformation carries with it the other components of the pallial map, which result similarly stretched into a curved inverted C-shaped arrangement. Each pallial region nevertheless maintains its fundamental dorso-ventral and rostro-caudal topology throughout the ensuing morphogenetic process. Abbreviations: pallial/subpallial boundary (psb), pallidum (Pal), striatum (Str), diagonal domain (Dg), preoptic area (Poa), pallial septum (SeP), subpallial septum (SeSP), olfactory bulb (olb). This figure was adapted from an illustration in Nieuwenhuys et al. (2008).
