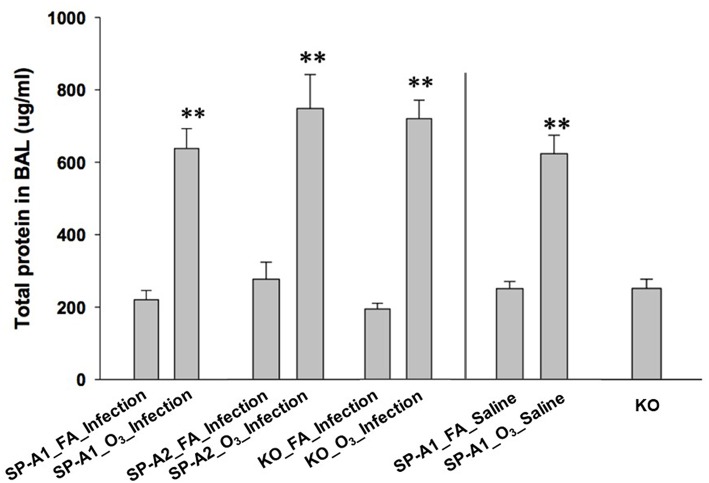
Figure 1.
Comparison of total protein concentration in the BAL fluid from exposed and infected mice. Three genotypes of mice (hTG SP-A1 and SP-A2 mice and SP-A KO mice) were exposed to ozone (3 ppm) or filtered air for 3 h and then intratracheally infected with 50 μl of bacterial solution (containing about 450 CFU of K. pneumoniae, control with 50 μl of saline). After 24 h of infection the mice were sacrificed and the lungs were subjected to BAL. Total protein concentration was determined in the supernatant of BAL. The results indicate that the total protein level of ozone-exposed mice, regardless of bacterial infection or saline control was significantly higher than that of FA-exposed mice (**p < 0.01). No significant difference is found among FA-exposed mouse groups regardless of infection or saline control, or among ozone-exposed mouse groups regardless of infection or saline control. In addition, no significant differences in total protein level in the BAL fluid are observed between KO background control and FA-exposed mice regardless of infection or saline control (The experimental groups and controls were separated by a vertical line).