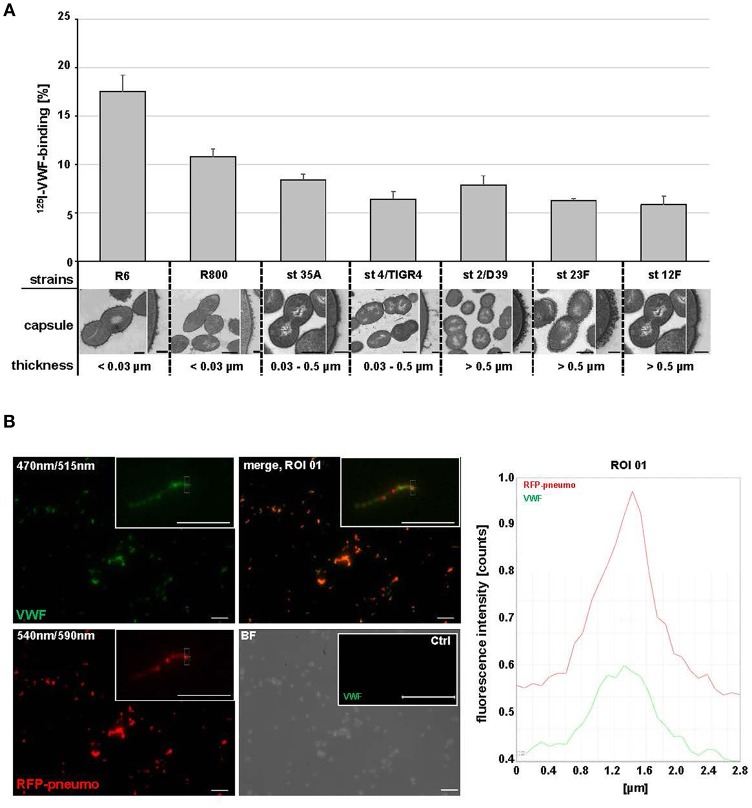
Figure 1.
Streptococcus pneumoniae binds human plasma VWF. (A) Binding analyses with radioactive labeled VWF and seven S. pneumoniae strains: R6, R800 and the serotypes (st) 35A, 4 (TIGER4), 2 (D39), 23F and 12F. VWF binding was expressed as percentage of total radioactivity added. Amount of capsular polysaccharides (CPS) was categorized according to the CPS-diameter determined by electron microscopic visualization: low encapsulation <0.03μm, middle encapsulation in a range of 0.03–0.5μm and high encapsulation >0.5μm. Scale bars represent 0.5 μm in the overview figures and 0.1 μm in magnified sections. (B) Immunofluorescence visualization of VWF binding to RFP-expressing pneumococci with FITC-conjugated VWF-specific antibodies after embedding of VWF-incubated pneumococci in agarose. RFP-expressing bacteria appear in red at 540/590 nm and VWF-detection is visualized in green at 470/515 nm. VWF coated bacteria appear in yellow in the merged channel. The insets visualize a representative fluorescence signal at 3-fold magnification. Antibody controls revealed no unspecific VWF-signal detection on the surface of pneumococci (Ctrl). Scale bar represents 10 μm. Fluorescence intensity determination visualizes the VWF-bacterial colocalization within the region of interest (ROI 01).