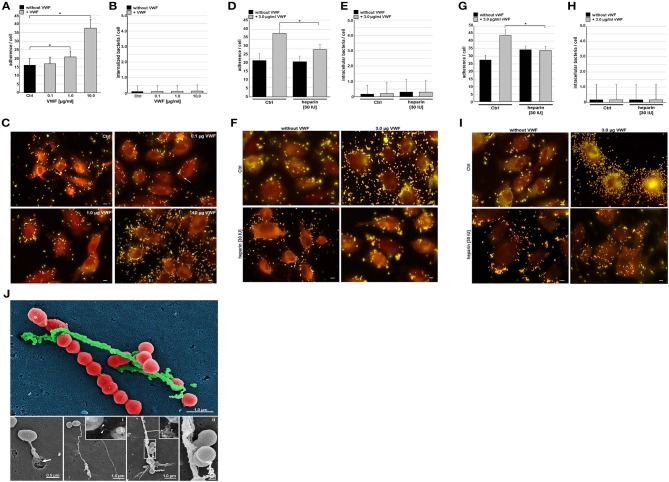
Figure 2.
VWF mediates pneumococcal adherence to endothelial cells. Microscopic determination of VWF-mediated bacterial adherence to subconfluently grown endothelial cells (HUVEC) and internalization after immunofluorescence staining with pneumococcus-specific rabbit antibodies followed by Alexa 488 and Alexa 568-conjugated secondary antibodies. HUVEC were pre-incubated with 0.1, 1.0, and 10.0 μg/ml VWF. Three independent assays were conducted in triplicate. After visual control of cell morphology and staining efficiency, number of yellow fluorescent attached bacteria (A) and number of red fluorescent internalized bacteria (B) were counted for a minimum of 50 endothelial cells in each sample. Representative images are shown in (C). White arrows indicate detection of internalized pneumococci. Scale bar represents 10 μm. Quantification of bacterial adherence (D) and internalization (E) in cell culture inhibition studies with 3.0 μg/ml VWF in presence of 30 IU heparin. Adherence and internalization were microscopically determined as described above (F). All data shown in Figure 2 represent mean values ± SEM; statistical significance was evaluated by unpaired Student's t-test (*p < 0.05 was defined as significantly different). Scale bar represents 10 μm. Effect of heparin on extent of VWF-mediated bacterial attachment (G,I) and internalization (H,I) was further determined after VWF-pre-incubation of bacteria instead of HUVEC. All data shown in Figure 2 represent mean values ± SEM; statistical significance was evaluated by unpaired Student's t-test (*p < 0.05 was defined as significantly different). Scale bar represents 10 μm. (J) Electron microscopic visualization of pneumococcus attachment to protein strings on HUVEC. Samples were subjected to field emission scanning electron microscopic visualization with a Zeiss Merlin FESEM, which illustrates pneumococcal attachment to long protein strings resembling VWF-strings in length and size. Colors have been applied by Adobe Photoshop CS5 v12.0 for emphasizing structural differences. RFP-expressing pneumococci are colorized in red, HMW VWF protein strings appear in green and the HUVEC cell background appears in dark blue. The white arrow in the lower left image points to a diplococcus bound to a VWF protein string, which is released by a secretory pod on the cell surface. The two insets visualize a VWF-specific immune-gold staining of a long, thin VWF-string (i) and of a short VWF string (ii). The gold-conjugated particle are marked with white arrow heads. The lower right picture shows a 5-fold magnification of the region marked with a white square. Scale bars of the insets represent 0.2 μm, the other scale bars are depicted in illustrations.