Figure 5.
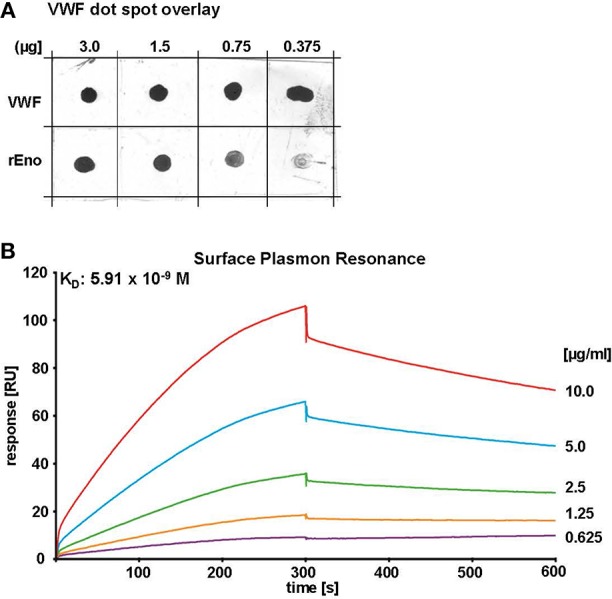
Enolase of S. pneumoniae binds VWF derived from human plasma with high affinity. (A) VWF dot spot overlay of recombinant enolase protein (rEno) of S. pneumoniae and VWF which were immobilized by dot spotting onto nitrocellulose in indicated amounts (VWF was used as positive control). Dose-dependent VWF-binding signals to rEno were detected by VWF-specific antibodies and visualization by chemiluminescence. Antibody controls are shown in Figure S1A. (B) Binding kinetics of rEno and plasma-derived VWF were determined by SPR using rEno as immobilized ligand on CM5 Biacore Chips and plasma VWF as analyte in concentrations of 0.625–10 μg/ml. Data evaluation was determined in two independent analyses using a 1:1 Langmuir model and revealed an average dissociation constant KD of 5.36 × 10−9 M at a Chi2-value of 0.665. Kinetic determination was performed with a BIACORE®T200 (GE Healthcare) at a flowrate of 10 μl per min. A representative sensorgram is shown.
