Figure 1.
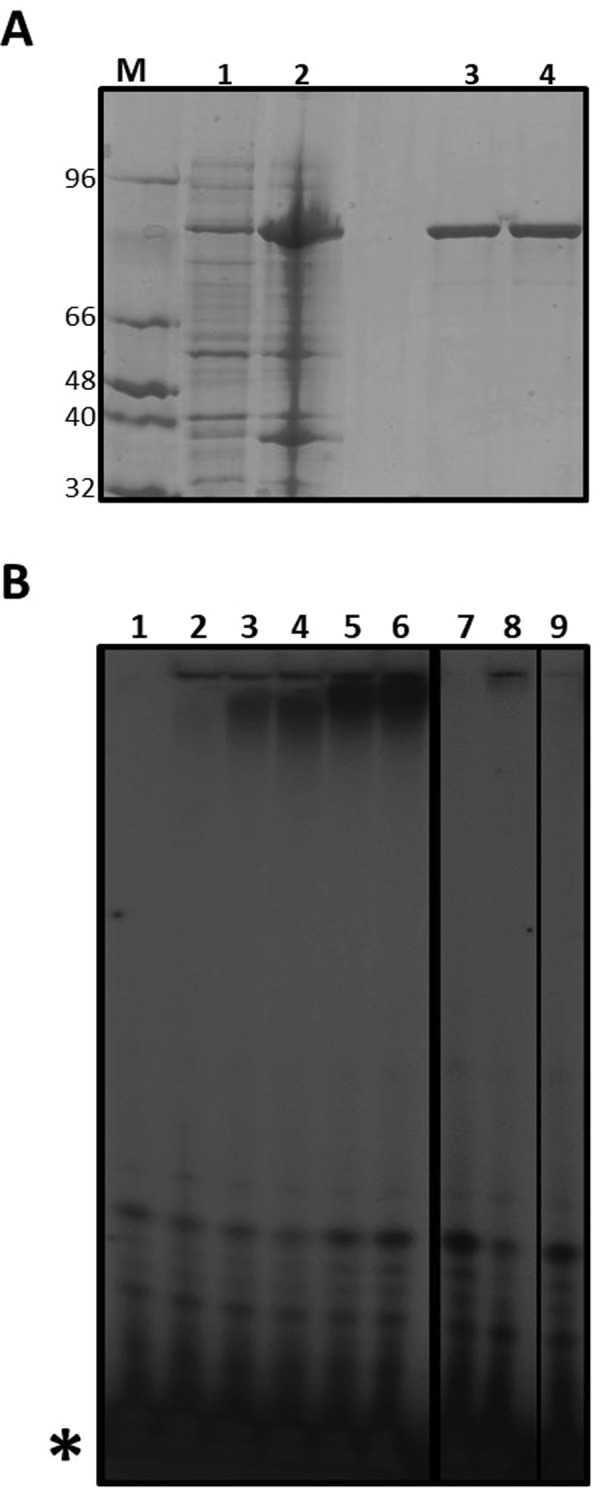
Purification of ZIKV NS5 RdRp and determination of polymerase activity. (A) SDS-PAGE analysis of ZIKV NS5 RdRp domain expressed in E. coli and purified by affinity chromatography. Lysates of E. coli BL21(DE3)-pRIL containing plasmid pET16a-ZIKV-NS5 and grown in the absence (lane 1) or presence (lane 2) of 500 μM IPTG. ZIKV RdRp wild-type (lane 3) and ZIKV RdRp GNN inactive mutant (lane 4) were obtained after purification through Ni-NTA resin. M, molecular marker. The molecular weight of each band is indicated (in kDa). Procedures for protein expression and purification are described in Methods. (B) Representative electropherogram of polymerization reactions carried out by ZIKV RdRp in the presence of [α-32P]ATP, using poly-U as template and MnCl2 as a metal donor. Reactions were stopped at increasing time points (from 0 to 3 hours; lanes 2 to 6). Polymerization assays performed in the absence of enzyme (lane 1), in the presence of MgCl2 as metal donor (lane 7), in the absence of any metal donor (lane 8), or using the GNN polymerase mutant (lane 9) are shown. Gel electrophoresis and visualization by autoradiography analysis were performed as described in Methods. The position of labeled nucleotides not incorporated in the RNA is indicated (*). A thick vertical line separates images obtained from independent gels. Both gels were run and autoradiographied using the same experimental conditions. A thinner black line separates two images cropped from the same gel but which were located in non-contiguous positions.
