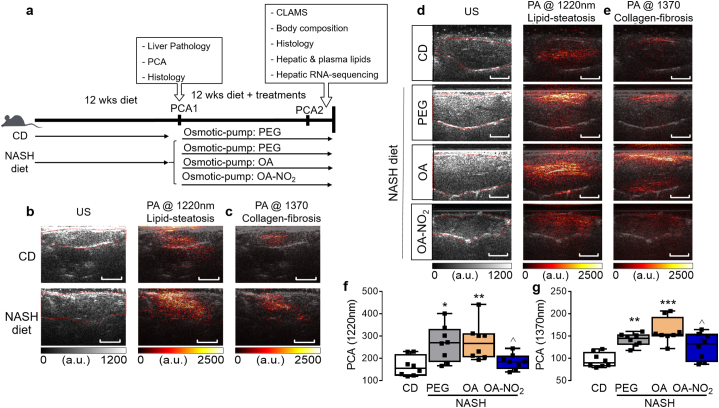
Fig. 1.
Non-invasive diagnosis reveals OA-NO2 protection against NASH-diet induced hepatic steatosis and fibrosis. (a) Experimental design: Steatohepatitis was induced in C57BL/6 mice by a NASH diet, rich in saturated fat, trans fat, fructose and cholesterol for 12 weeks. After 12 weeks, high-resolution physio-chemical analysis ultrasound (PCA-US), confirmed coexistence of lipid steatosis and early fibrosis. Then, osmotic minipumps were implanted subcutaneously to deliver PEG, OA or OA-NO2 (5 mg/kg/d) for additional 12 weeks under chow diet (CD) or NASH-diet feeding (4 groups, n = 10 per group). Established liver damage was confirmed in a subpopulation (n = 3) analyzed after 12 weeks using (b) conventional ultrasound (US) combined with high-resolution PCA high-resolution at 1220 nm optical wavelength to detect hepatic lipids, and (c) at 1370 nm optical wavelength to quantify hepatic collagen content. Two weeks before terminal analysis of liver pathology PA-US was used to quantitatively analyze lipid content and total collagen content in the NASH-diet model. High-resolution PCA demonstrated a marked reduction of total hepatic lipid (d) and collagen content (e) upon OA-NO2 treatment compared to non-nitrated OA. Quantitative analysis of PA absorption from each experimental group at 1220 nm (f) and 1370 nm fingerprint (g). Size bars = 5 mm Data is plotted as box and whiskers from minimum to maximum values showing all points. *p < .05, **p < .01, ***p < .001 vs. CD; ^p < .05, vs. NASH OA. n = 8.