Fig. 2.
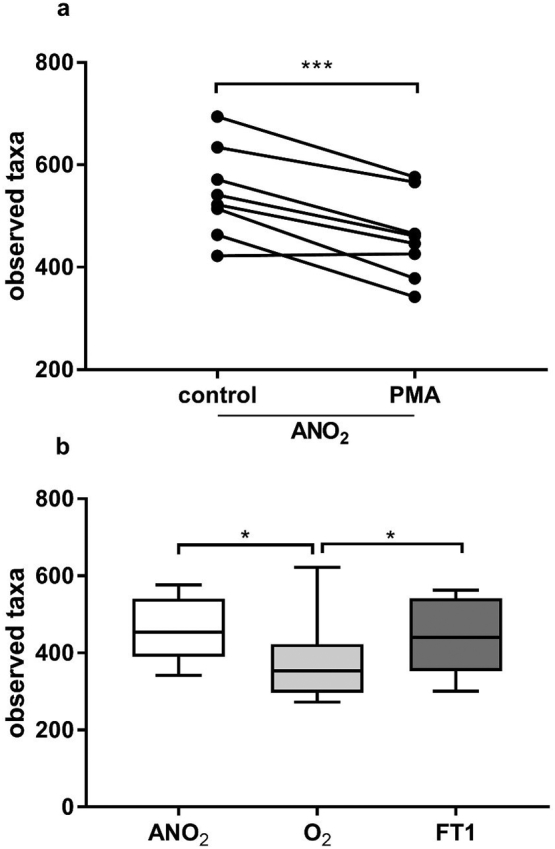
Taxa richness of faecal microbiota transplant material from 8 donors as assessed by 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing with and without PMA treatment. Viable diversity (PMA treated group) was significantly lower than diversity observed in control specimens, even in samples processed immediately in anaerobic conditions (Fig. 2a ***=p<0·001, paired t-test). When comparing only viable diversity between samples processed in anaerobic conditions (ANO2), in ambient air (O2), or after one cycle of freezing and thawing in anaerobically processed specimens (FT1) there are significantly lower observed species in specimens processed O2, whereas freeze-thawing of specimens did not significantly reduce diversity (Fig. 2b, box plot depicts median and IQR and error bars depict minimum to maximum values; *= p<0·05; Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test).
