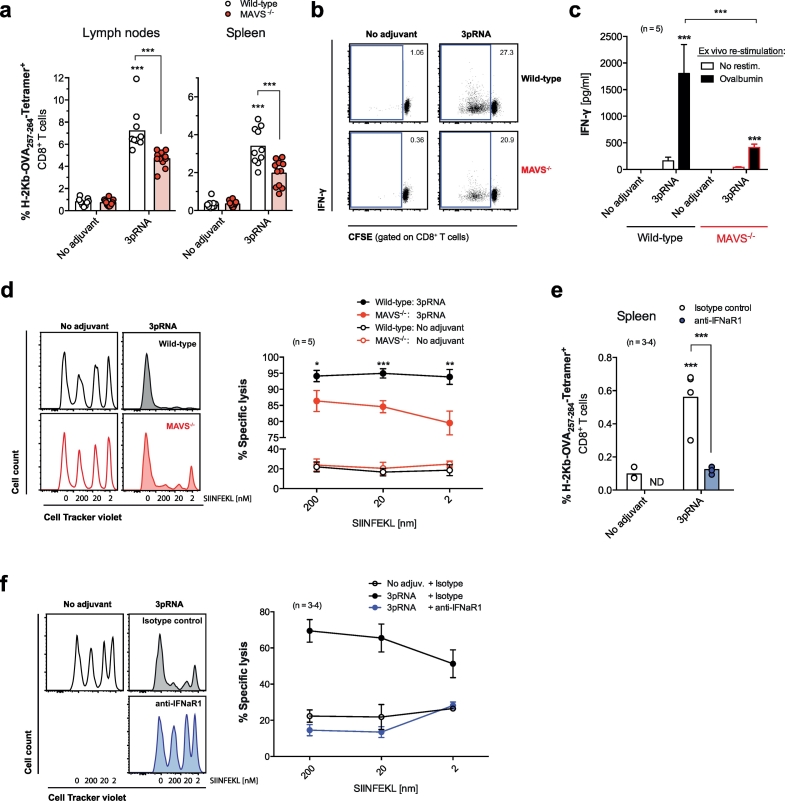
Fig. 3.
The RIG-I / MAVS / IFN-I pathway induces robust cross-priming of cytotoxic T cells in vivo. WT and MAVS-deficient mice were injected sc with OVA +3pRNA twice. (a) Frequency of H-2Kb-SIINFEKL Tetramer+ cytotoxic T cells in draining lymph nodes (LN) and spleen. Each data point represents one individual of at least n = 10 mice and the mean per group is depicted as a bar. (b) Representative blots are gated on CD8+ T cells from ex vivo OVA restimulated LN cell cultures and give the percentage of proliferating cells. (c) IFN-γ levels from the above cultures. Data give the mean ± S.E.M. of n = 5 independent cell cultures per group each derived from individual mice. (d) In vivo cytotoxic activity was measured by target cell elimination of fluorescently labeled, SIINFEKL peptide-pulsed syngenic splenocytes. Histograms show the frequency of transferred target cells in the spleen of a representative recipient mouse. Numbers give the concentration [nm] of SIINFEKL-pulsing and thus the immunogenicity of the indicated target cell population. The graph shows mean specific lysis ± S.E.M. of n = 5 individual mice. (e-f) WT mice were vaccinated iv with OVA +3pRNA once and were additionally treated with anti-IFNaR1 blocking antibody one day prior to vaccination. (e) Frequency of H-2Kb-SIINFEKL Tetramer+ cytotoxic T cells in the spleen and (f) cytolytic activity were analyzed as described above (individual mice, n = 3 for the ‘no adjuvant’ and n = 4 for the ‘3pRNA’ group). All data are representative of at least two independent experiments. (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) for multiple comparisons). ND, not determined.