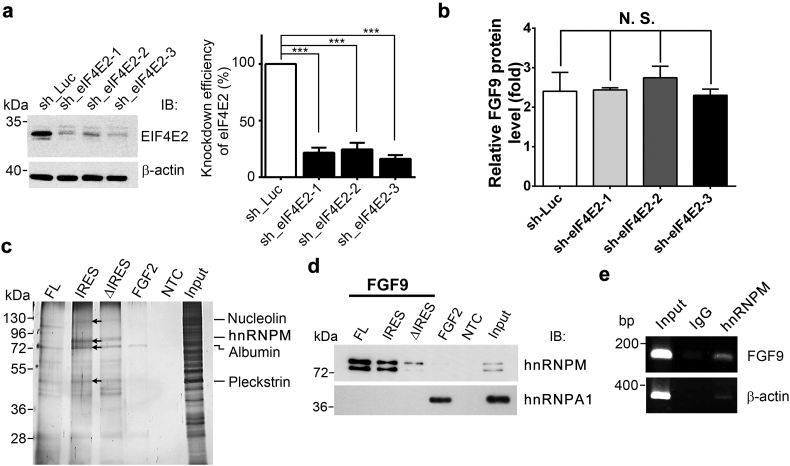
Fig. 1.
hnRNPM is a novel FGF9 IRES-binding protein. (a) Immunoblot of HEK293 cells expressing control shRNA (sh_Luc) or three eIF4E2-specific shRNAs (sh_eIF4E2–1–3, left). Relative knockdown efficiency of each shRNA compared to sh_Luc was shown (right). The bars represent the mean ± SEM (n = 3). ⁎⁎⁎P < .001 (ANOVA followed by Tukey's multiple test). (b) FGF9 ELISA shows that all three eIF4E2-specific shRNAs knockdown do not change the FGF9 protein production during hypoxia (n = 3). (c) A silver stain image representing unique proteins identified by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry (indicated by arrows). The Input and NTC were used to show the target proteins in the cell lysates and a negative control for the pull-down assay. (d) Alignment of peptide sequences from LTQ-Orbitrap analysis matched to the human hnRNPM protein sequences. (e) Immunoblot of hnRNPM and hnRNPA1 that were pulled down by indicated biotinylated probes. The FGF2/hnRNPA1 and NTC were used as positive and negative controls for the pull-down assay. Input was used to show the target proteins in the cell lysates. (f) Representative gel image shows that FGF9 mRNAs specifically interact with hnRNPM. β-actin and normal mouse IgG were used as a control transcript and a negative control, respectively for RNA immunoprecipitation assay.