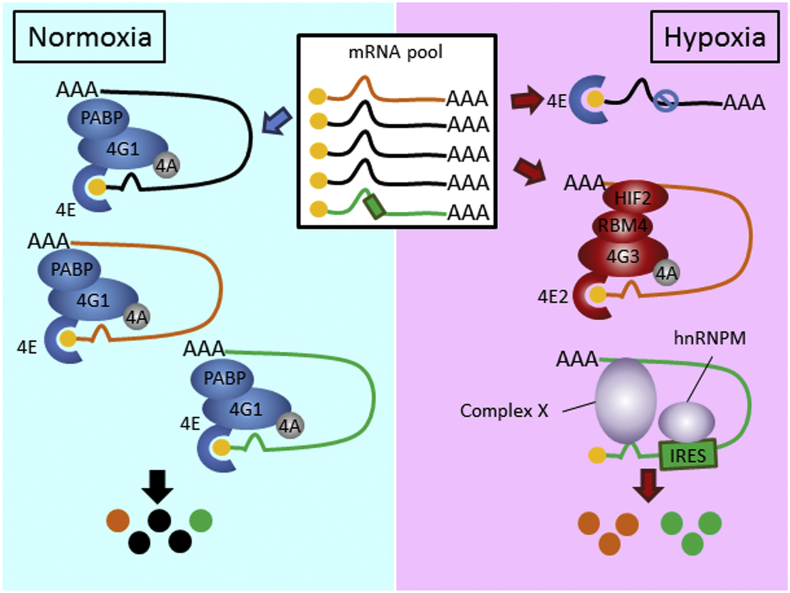
Fig. 7.
A working model of hnRNPM-IRES-mediated translational switch in hypoxia. There are 3 types of cytoplasmic mRNAs (labeled with different colors) in the mRNA pool in the cells. Cap-dependent translation carried out by eIF4F (eIF4E-eIF4A-eIF4G1) is predominately used for protein synthesis in normoxia (left). When eIF4F-dependent translation is inhibited during hypoxia (transcripts in black), mRNA translation is then carried out selectively by the hypoxic eIF4F (eIF4E2-eIF4A-eIF4G3)-dependent (transcripts in orange) pathway [5] (right). Alternatively, a subset of IRES-containing mRNAs (transcripts in green) undergoes conformational change in hypoxia and is recognized by the novel hypoxia-induced ITAF hnRNPM. Together with the help from complex X (other RBPs like hnRNPC1/C2 and HuR) and the interaction of hnRNPM-IRES trigger the formation of a new translation initiation complex and prime cap-independent translation to take place (right). Overall, protein synthesis through co-regulated, co-occupied IRES-containing mRNAs by hnRNPM can achieve vital physiological responses to combat environmental hypoxic stress. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)