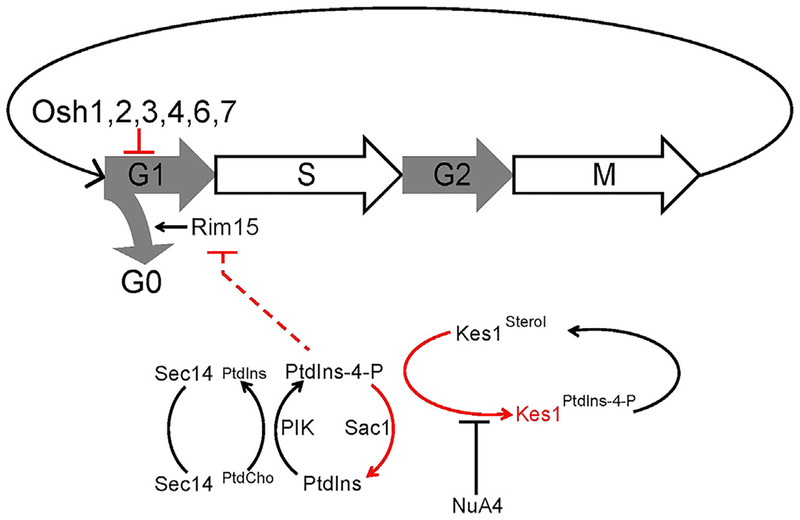
Figure 7. A Sec14/Kes1 PtdIns-4-P Signaling Axis in Cell-Cycle Control.
Heterotypic PtdCho/PtdIns exchange defines the machine by which Sec14 stimulates PtdIns 4-OH kinase-mediated production of a PtdIns-4-P pool that regulates progression through the G1 phases of the cell cycle. This signaling is antagonized by activity of the Sac1 PtdIns-4-P phosphatase and Kes1 binding and sequestering PtdIns-4-P from its effectors. The Kes1 brake is itself tuned by a heterotypic sterol/PtdIns-4-P exchange cycle and the activity of NuA4 KAT in acetylating K109. The Sec14/Kes1 checkpoint requires activity of the Rim15 kinase, and we propose this PtdIns-4-P pool is produced in a TGN/endosomal compartment. Functionally distinct, roles for other Osh proteins (other than Osh5) in regulating G1 progression are also indicated. Pathway brakes are highlighted in red.