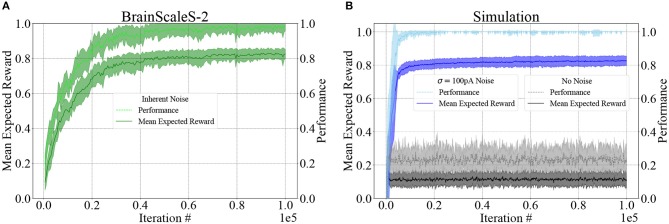
Figure 5.
Learning results for BSS2 and the software simulation using NEST, in terms of Mean expected reward (Equation 8) and Pong performance (Equation 9). In both cases, we plot the mean and standard deviation (shaded area) of 10 experiments. (A) BSS2 uses its intrinsic noise as an action exploration mechanism that drives learning. (B) The software simulation without noise is unable to learn and does not progress beyond chance level. Adding Gaussian zero-mean current noise with σ = 100 pA to each neuron allows the network to explore actions and enables learning. The simulation converges faster due to the idealized simulated scenario where no fixed-pattern noise is present.