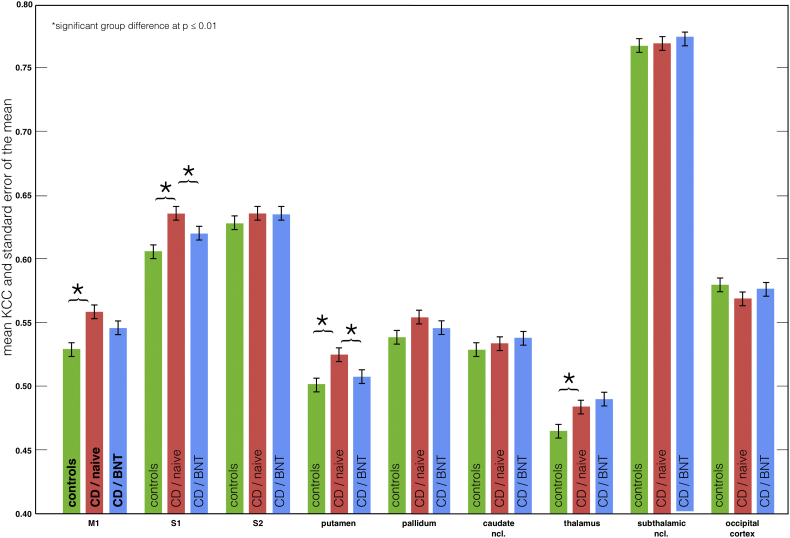
Fig. 3.
Regional homogeneity analysis in cervical dystonia (CD) and effects of treatment with botulinum toxin (BNT).
Kendall's coefficient of concordance (KCC) and standard error of the mean of the defined ROIs in the primary motor cortex (M1), the primary and secondary somatosensory cortex (S1 / S2), the BG, and the thalamus in the controls and the CD patients without (naive) and with BNT (6 month) treatment. In CD (naive) KCC values were significantly increased (p ≤ 0.01, 2-samples t-test: red vs. green) in M1, S1, putamen, and thalamus (compared to healthy controls). With BNT treatment KCC values in CD were again significantly decreased (p ≤ 0.01, paired t-test: blue vs. red) in S1 and putamen. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)