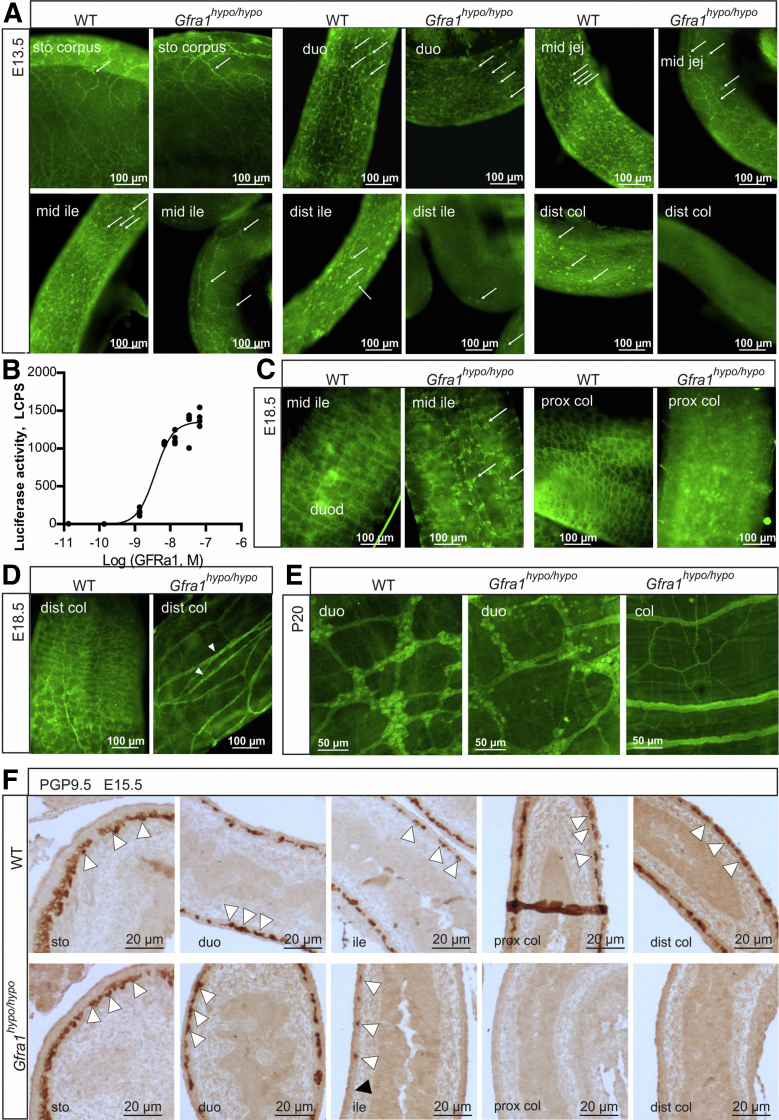
Figure 2.
Impaired enteric neuronal progenitor colonization and hypertrophic nerve fibers in the distal gut of GFRa1 hypomorphic mice. (A) Immunohistochemistry using the pan-neuronal marker ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase L1 in E13.5 WT and Gfra1hypo/hypo mice whole-mount GI tract preparations. Note the reduced numbers of neuronal progenitors (white arrows) beginning at the midjejunum of Gfra1hypo/hypo mice and the absence of neuronal progenitors from the distal and GDNF ileum onward; representative images are shown (N = 3–4 animals per genotype). (B) Dose-dependent activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling by soluble GFRa1. MG87 fibroblasts stably expressing RET and the PathDetect Elk-1 luciferase system were treated with the indicated concentration of soluble GFRa1 (N = 4 biological replicates per experiment; N = 2 experiments). (C and D) ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase L1 immunohistochemistry was performed in E18.5 WT and Gfra1hypo/hypo mice from whole-mount GI tract preparations, showing reduced and scattered innervation in the midileum, an absence of innervation in the proximal colon, and hypertrophic fibers in the distal colon (white arrowheads, a hallmark feature of HSCR); the white arrows indicate neuronal somas. Representative images are shown (N = 3–4 animals per genotype). (E) ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase L1 immunohistochemistry performed on P20 whole-mount myenteric plexus preparations showing normal innervation in the duodenum, an absence of neuronal cell bodies in the colon, and hypertrophic fibers in the colon of Gfra1hypo/hypo mice; representative images are shown (N = 2–3 animals per genotype). (F) The ENCC colonization of the mouse hindgut is complete by E14.5. Representative image of sagittal gut sections immunostained with the pan-neuronal marker ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase L1 in E15.5 WT and Gfra1hypo/hypo mice, showing that the enteric neuronal progenitors have reached the distal colon in the WT mice (white arrowheads); in contrast, enteric neuronal progenitors reached the proximal ileum (white arrowheads) in E15.5 Gfra1hypo/hypo mice, but are absent from the distal ileum, cecum, and colon. The point at which aganglionosis begins is indicated by a black arrowhead; representative images from WT and Gfra1hypo/hypo mice are shown. dist, distal; duo, duodenum; ile, ileum; jej, jejunum; prox, proximal.