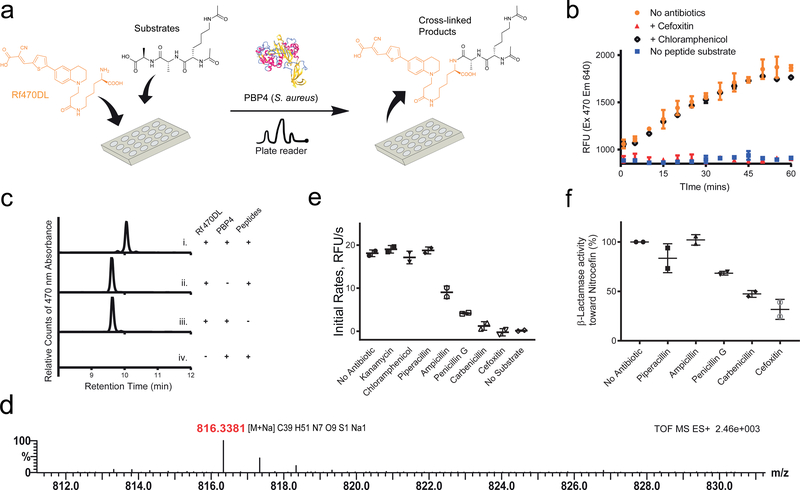
Figure 4. RfDAAs facilitate real-time in vitro transpeptidation assays.
a) Scheme of assay procedure. Rf470DL and the synthetic substrate were mixed in a 96-well plate. The fluorescence intensity of Rf470DL was then measured over time upon the addition of recombinant S. aureus PBP4. b) Real-time monitoring of Rf470DL intensity. An intensity increase was observed in the assay; while adding PBP inhibitors blocked the reaction. c) HPLC analysis of the assay products. A shifted retention time was observed when the Rf470DL-substrate mixture was treated with PBP4. d) High-resolution MS analysis of the products from the assay confirmed the formation of the cross-linked product. e) Screening of antibiotic effect on S aureus PBP4 activity. A 1:10 ratio of antibiotics to the substrate was used in the experiments. Kanamycin and Chloramphenicol (ribosome inhibitors) did not inhibit the Rf470DL incorporation. Piperacillin, Ampicillin, Penicillin G, Carbenicillin and Cefoxitin (β-lactam antibiotics) showed different level of inhibition. f) β-lactamase activity of S. aureus PBP4. A competition assay using Nitrocefin was performed to study PBP4 β-lactamase activity toward the β-lactam antibiotics used in the assay experiments. In this panel, low activity stands for a strong inhibition effect of the antibiotics toward PBP4, and vice versa. Values are normalized to the “no antibiotic” sample. Error bars: Mean value and standard deviation.