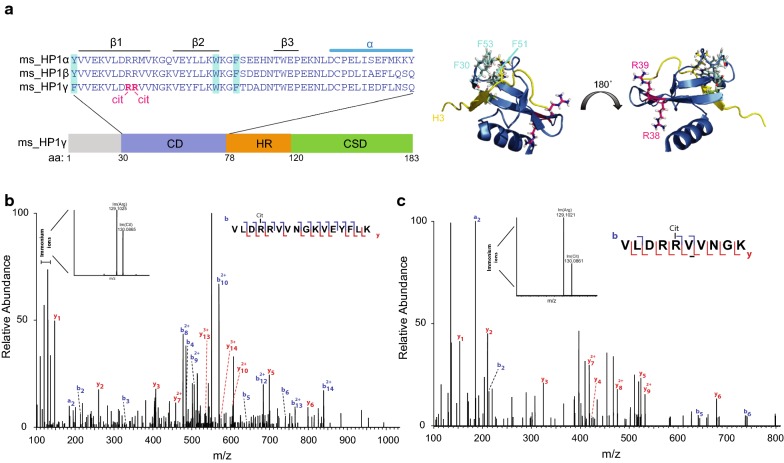
Fig. 1.
HP1γ chromodomain is citrullinated in vivo. a The left panel is a schematic illustration of the functional domain structure of mouse HP1γ. Chromodomain (CD, blue), hinge region (HR, orange), chromoshadow domain (CSD, green) and N-terminal extension (grey) are indicated. Above is a multiple sequence alignment of mouse HP1 paralogue chromodomain amino acid (aa) sequences using Clustal Omega. CD secondary structures are indicated above the sequences, and residues forming the hydrophobic H3K9me3 binding pocket [5] are highlighted in turquois. Citrullinated residues are highlighted in pink. The right panel shows an X-ray crystal structure of the HP1γ CD in complex with H3K9me3. PDB file ‘5tli’ was adapted using Pymole. Residues forming the hydrophobic pocket are highlighted in turquois and citrullinated residues in pink. b/c MS/MS analysis identifies citrullination of HP1γ at residues R38 and/or R39 in a chromatin fraction of mESCs. Plots show the fragmentation spectra of the LysC peptides VLDRRVVNGKVEYFLK (b) and VLDRRVVNGK (c) surrounding arginine (R) 38 and R39 of HP1γ. The y (red) and b (blue) series indicate fragments at amide bonds of the peptide. Immonium ions unique for citrulline (Im/(Cit) at m/z 130) and arginine (Im/(Arg) at m/z 129) were detected in both peptides