Fig. 1.
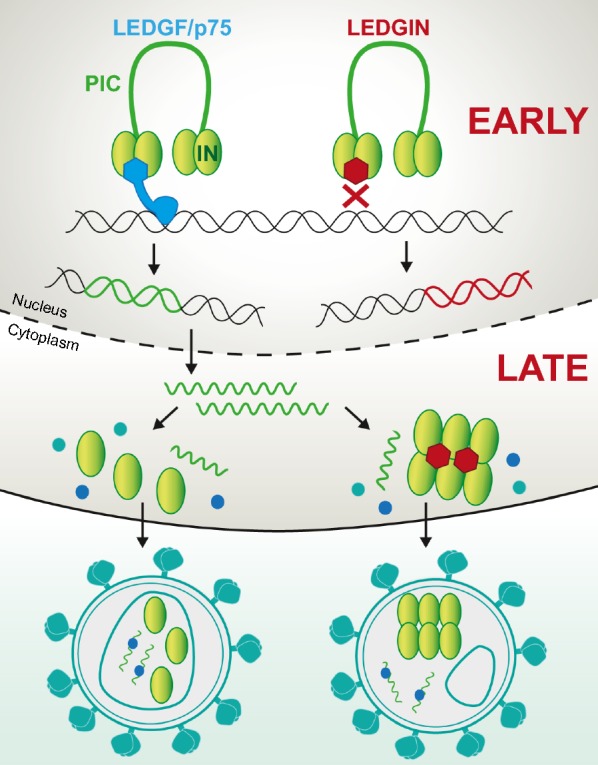
Early and late effects of LEDGINs. LEDGINs inhibit the interaction between the HIV integrase (IN) and the cellular co-factor LEDGF/p75 by binding to the IN dimer interface. This leads to an allosteric inhibition of integration during the early replication steps (early effect; upper panel) [58, 63]. In addition, it relocates integration of residual integrants out of transcription units resulting in more latent provirus [57]. LEDGINs also affect late replication steps; LEDGINs enhance IN oligomerization resulting in maturation defects (late effect; lower panel) [64–67]. These progeny viruses lack the capsid core or the ribonucleoprotein is located outside of the core and are less infectious
