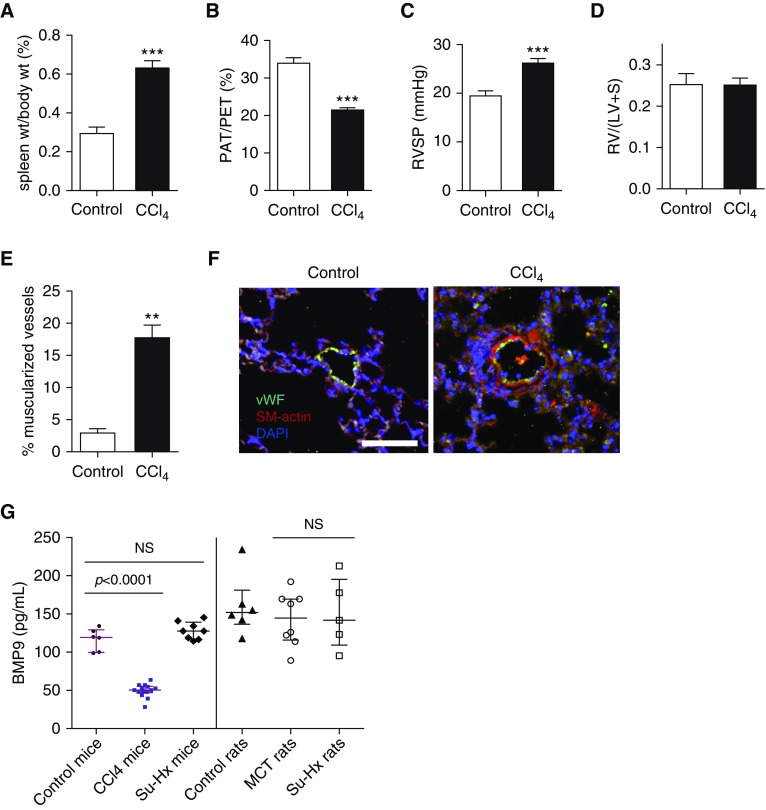
Figure 4.
Mice with portal hypertension exhibit mild pulmonary hypertension and reduced levels of circulating BMP9 (bone morphogenetic protein 9). Male C57BL/6 mice aged 6–8 weeks (n = 9) were treated with phenobarbital (0.35 g/L) via drinking water and CCl4 in olive oil (1:5; 0.4 ml/kg body weight, i.p. 3 times/wk) or vehicle (n = 10) for 16 weeks, at the end of which they underwent right heart catheterization. Two groups were compared using unpaired Student’s t test. (A) CCl4-treated mice develop splenomegaly because of portal hypertension based on elevated spleen to body weight ratio versus vehicle-treated animals. (B) Cardiac ultrasound demonstrates presence of pulmonary hypertension in CCl4-treated mice based on a reduced ratio of pulmonary artery acceleration time to pulmonary ejection time. (C) CCl4-treated mice develop mild pulmonary hypertension based on a mild but significant increase in right ventricular systolic pressure compared with control animals. (D) There was no difference in right ventricular hypertrophy between control and CCl4-treated mice. (E and F) Quantification and representative photomicrographs of immunofluorescence of lung sections for von Willebrand factor and smooth muscle α-actin revealed increased muscularization of small (≤50 μm) arterioles in CCl4-treated mice (bar = 100 μm). (G) Levels of circulating BMP9 were significantly lower in mice treated with CCl4 for 20 weeks (n = 14) than control mice (n = 6) (one-way ANOVA with Dunnett multiple comparison), comparable with decreased levels observed in patients with portopulmonary hypertension. Compared with control mice, levels of BMP9 were unchanged in mice treated with SUGEN/hypoxia (Su-Hx; n = 8). Similarly, compared with control rats, BMP9 levels were unchanged in rats treated with monocrotaline (n = 8) or Su-Hx (n = 5) (one-way ANOVA with Dunnett multiple comparison). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM, with P values given in the figure or by asterisks as follows: **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001. LV = left ventricle; MCT = monocrotaline; NS = not significant (P > 0.05); PAT = pulmonary artery acceleration time; PET = pulmonary ejection time; RV = right ventricle; RVSP = right ventricular systolic pressure; S = septum; SM-actin = smooth muscle α-actin; vWF = von Willebrand factor; wt = weight.