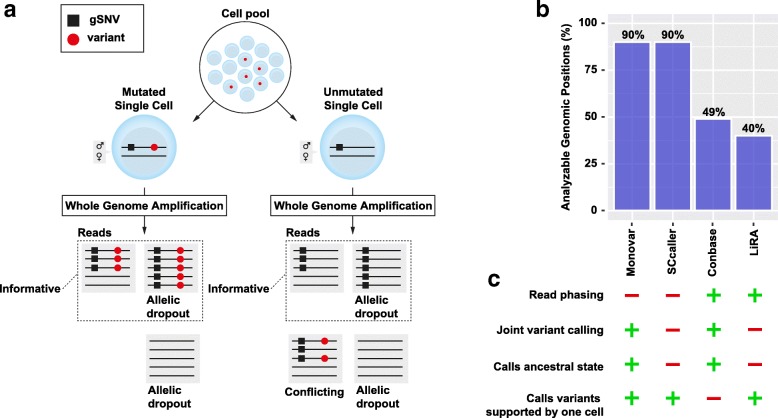
Fig. 1.
a Somatic mutations are present in a subset of a population of cells and can be identified by DNA sequencing of whole genome amplified single cells. WGA may result in allelic dropout, which in turn may result in false negative variant calls if dropout has occurred of the mutated allele. False positive variant calls may arise from amplification errors or alignment artifacts among molecules with high sequence similarity, resulting in conflicting haplotype observations. Conbase circumvents these problems by determining locus-specific allelic dropout individually per sample and analyzes concordance of the observed haplotypes across the cell population. b The percentage of genomic positions that are analyzable by Conbase, Monovar, SCcaller, and LiRA. Genomic positions analyzable for Monovar and SCcaller were defined as the fraction of bases covered by at least one read in an unamplified bulk sample sequenced at 40x coverage. Genomic positions analyzable for Conbase and LiRA were defined as the fraction of unique genomic positions present within 650 bp of gSNVs. c Overview of some features of Conbase, Monovar, SCcaller, and LiRA