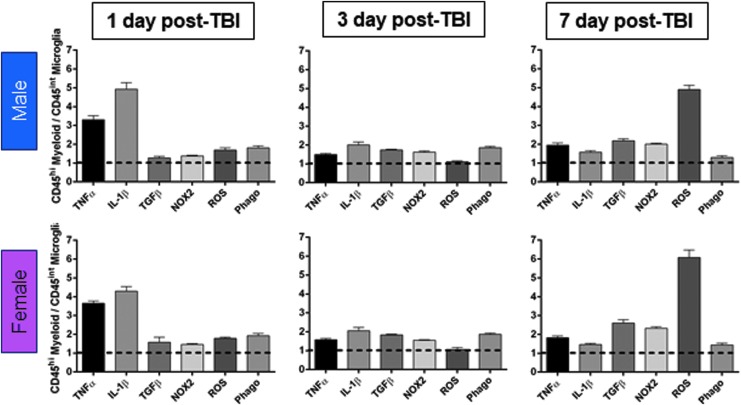
FIG. 5.
Infiltrating peripheral myeloid cells produce high levels of inflammatory cytokines and reactive oxygen species (ROS), and have high phagocytic activity following controlled cortical impact. Comparison of infiltrating myeloid cells (CD45hi) versus resident microglial (CD45int) levels of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) α, interleukin (IL)-1β, transforming growth factor (TGF) β, NOX2, ROS, and phagocytosis at each post-injury time-point. Males and females MFI values for each marker are represented at each time-point (1, 3, and 7 days post-injury) and are expressed as a relative CD45hi myeloid / CD45int microglia levels. After traumatic brain injury (TBI), infiltrating myeloid cells express higher levels of TNFα, IL1β, TGFβ, and NOX2 protein, produce more ROS, and have greater phagocytic ability than resident microglia at each time-point. Student's t-test, p < 0.01 for all comparisons; n = 6-12/group. Color image is available online.