Extended Data Figure 4.
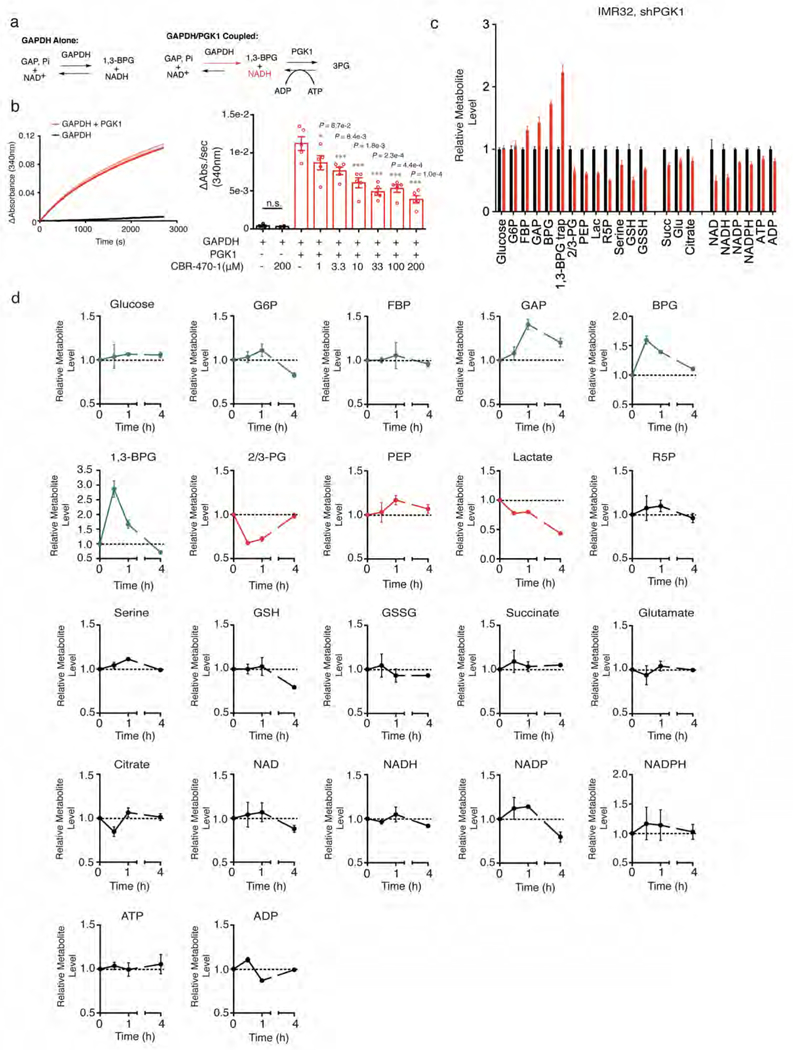
CBR-470-1 inhibits PGK1 in vitro and in situ. a, Schematic of the GAPDH/PGK1 coupled assay. Pre-equilibration of the GAPDH reaction (top left) results in an NAD+/NADH equilibrium, which upon addition of PGK1 and ADP pulls the reaction to the right producing more NADH. Monitoring NADH absorbance after addition of PGK1 (bottom right) can be used to monitor PGK1 activity in the forward direction (right). Kinetic monitoring of NADH absorbance (340 nm) after established equilibrium with GAPDH shows little change (black curve), but is significantly increased upon addition of PGK1, pulling the equilibrium to the right (red curve). b, CBR-470-1 does not affect the GAPDH equilibrium alone, but significantly inhibits PGK1-dependent activity and accumulation of NADH (n=5). c, d, Relative level of central metabolites in IMR32 cells treated with viral knockdown of PGK1 for 72 hours (c) (n=4) and with CBR-470-1 relative DMSO alone for the indicative times (d) (n=3). Each metabolite is normalized to the control condition at each time point. Univariate two-sided t-test (Extended Data Fig 5b); data shown represent mean ± SEM of biologically independent samples.
