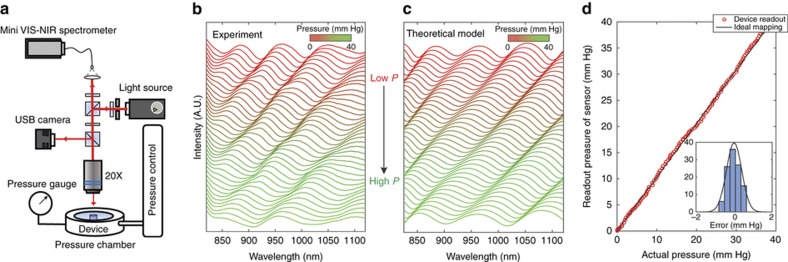
Figure 2.
Sensor characterization in a controlled pressure chamber. (a) Intraocular pressure (IOP) sensor characterization in a controlled pressure chamber with a digital pressure gauge. A schematic of the sensor optical resonance detector is shown above the pressure chamber. (b) Experimentally determined spectra from the sensor in the pressure range from 1 to 40 mm Hg with the spectra corresponding to 1 mm Hg shown at the top and the spectra for 40 mm Hg shown at the bottom. The spectra for the intervening IOPs are shown in sequence from top to bottom. (c) Theoretically predicted spectra corresponding to the pressure range from 1 (top spectra) to 40 mm Hg (bottom spectra). (d) Highly linear, very close one-to-one matching between the sensor measurements (vertical axis) and the digital pressure-gauge readouts (horizontal axis). The black line shows a theoretical perfect match of sensor and digital pressure-gauge readings, and the red circles indicate actual experimental measurements corresponding to the pressure readout based on the optomechanical model (OMM). Histogram shows the error distribution (RMSE: 0.29 mm Hg). Even in the worst case, the sensor reading was within ±1 mm Hg of the digital pressure-gauge readings.