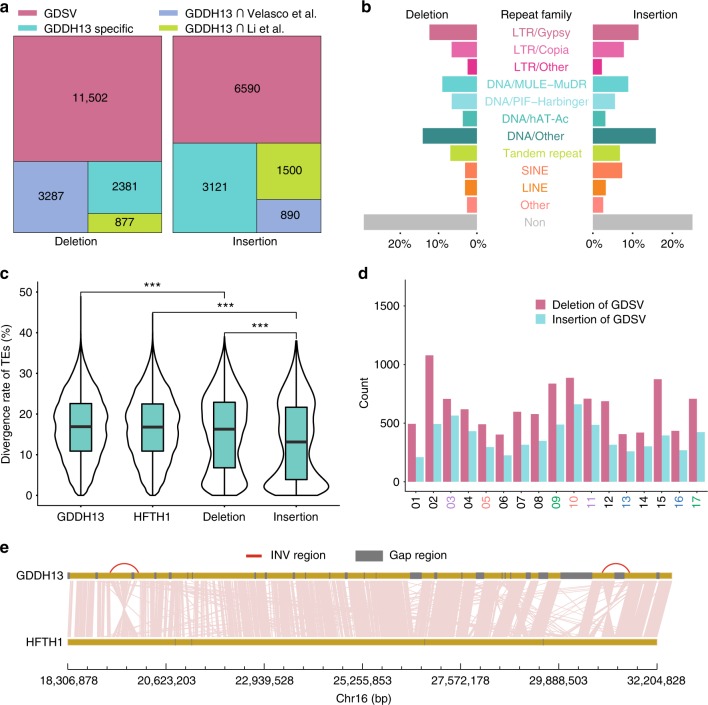
Fig. 2.
Characterisation of structural variants. a The overlap of structural variations ( > 100 bp) between GDDH13 and other published assemblies of Golden Delicious. b Classification of repeat elements associated with structural variations. A repeat element was defined as being associated with a structural variation if it overlaps with the structural variation. LTR, long terminal repeat; DNA, DNA transposon; SINE, short interspersed element; LINE, long interspersed element; Other, other types of repeat; Non, no repeats were detected. c Divergence rate of transposons of different sources. Deletion and insertion represent transposons associated with deletions and insertions, respectively. RepeatMasker was used to calculate the divergence rate from the consensus sequence of Repbase for each transposon. The middle hinge of all boxes is the median, the lower and upper hinges correspond to the 25th and 75th percentiles, and the whiskers represent the 1.5 inter-quartile range (IQR) extending from the hinges. Wilcoxon rank sum test, ***p < 0.001 and n = 435,202, 456,919, 6525, 4010 for GDDH13, HFTH1, Deletion, Insertion, respectively. d Count of structural variations detected in each chromosome. Duplicated chromosomes are shown in the x-axis with the same colour. e Synteny view of two large inversions with a length longer than 600 bp in chromosome 16 (19,782,372–20,450,041 and 31,388,523–32,032,862). Source data are provided in Source Data file 1