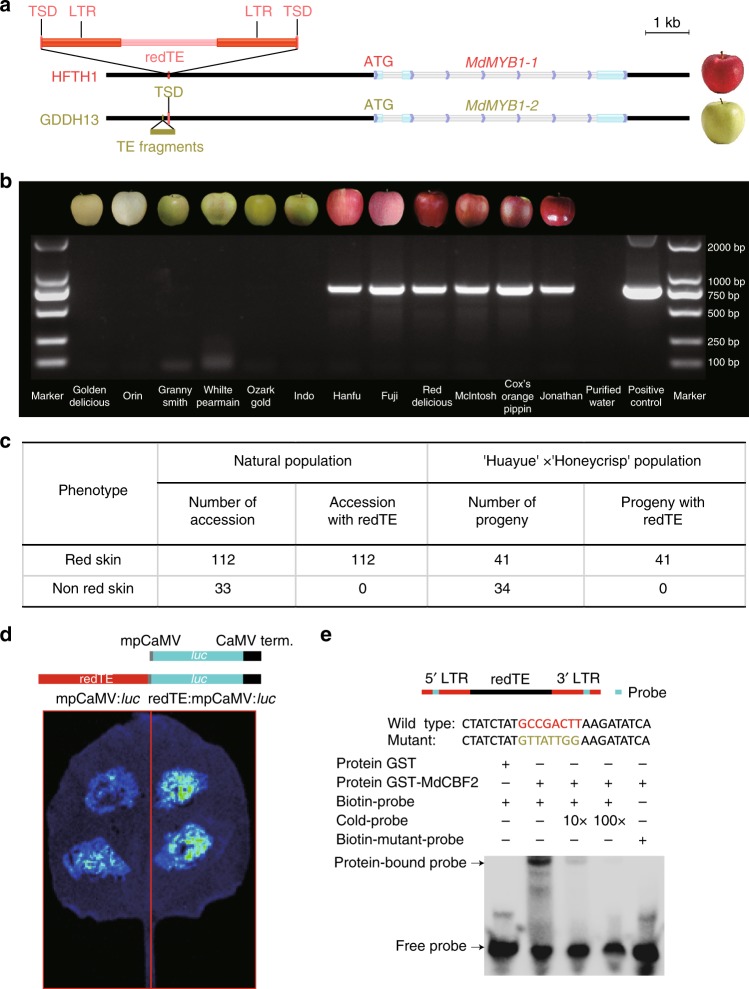
Fig. 4.
Red phenotype of apple associated with an LTR retrotransposon. a Molecular structure of MdMYB1-1 and MdMYB1-2 alleles with flanking sequences. The insertion sites upstream of MdMYB1-1 and MdMYB1-2 are indicated by a red line (HFTH1) and golden yellow line (GDDH13), respectively. b Images of 12 well-known apple varieties with non-red or red skin colour (upper panel) and PCR-based screen showing the absence (right) or presence (left) of the LTR retrotransposon insertion in the upstream of MdMYB1. A 750 bp fragment corresponding to the partial of redTE that is absent in non-red-skinned varieties (lanes 1 to 6) and is present only in red-skinned varieties (lanes 7 to 12). Lane 13, control check (purified water was used as the template), Lane 14, positive control. c PCR-based analysis of the redTE insertion in 145 accessions and the F1 segregating population from the cross of Huayue × Honeycrisp. d Constructs and transient expression assays showing that redTE obviously enhanced the luciferase expression levels. Upper panel, the mpCaM:luc (up) and redTE:mpCaM:luc (down) construct backbone consists of the minimal promoter from the cauliflower mosaic virus (mpCaMV, grey box), luciferase ORF and cauliflower mosaic virus terminator (black box). Lower panel, Luciferase image of Nicotiana benthamiana leaves 72 h after infiltration with the Agrobacterial strains containing mpCaM:luc (left), and redTE:mpCaM:luc (right), respectively. e MdCBF2 binds directly to the cis-acting element GCCGACTT. Source data of Fig. 4b, d are provided in Source Data file 1