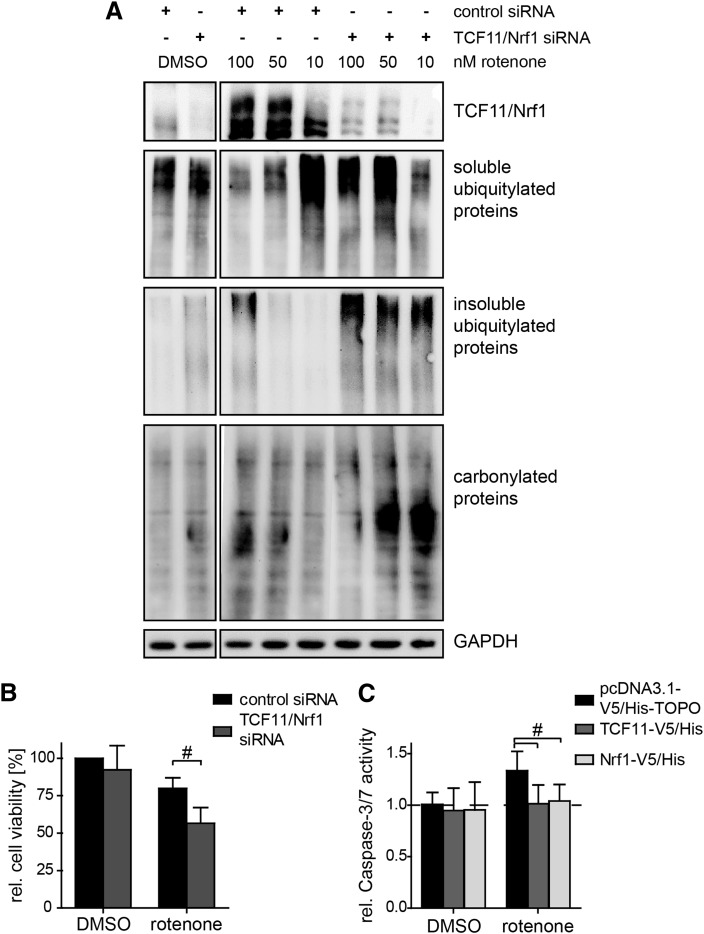
FIG. 7.
TCF11/Nrf1 diminishes rotenone-induced proteotoxic stress and cell death. (A) SH-SY5Y cells were treated with the rotenone concentrations indicated for 6 h and depleted or not for TCF11/Nrf1 by siRNA. Proteins were extracted by RIPA and were fractionated into detergent-soluble and detergent-resistant fraction by urea and stained for TCF11/Nrf1, GAPDH (loading control), ubiquitin conjugates, and carbonyls. TCF11/Nrf1 depletion cells promote the accumulation of ubiquitin conjugates in the detergent-resistant fraction. (B) For the final 20 h of a 48 h TCF11/Nrf1 depletion, SH-SY5Y cells were exposed to 1 nM rotenone and cell viability analyzed by XTT assay. Shown are the mean values of the relative cell viability ± SD from three independent experiments. (C) Cultured SH-SY5Y cells were transfected with TCF11-V5/His, Nrf1-V5/His, or pcDNA3.1-V5/His-TOPO and then exposed to 10 μM rotenone for 24 h. The caspase-3/7 activity was then measured. Shown are the mean values of the relative activity ± SD from nine replicates of three independent experiments. The overexpression was proofed by immunoblotting against the V5 tag, TCF11/Nrf1, and β-tubulin (#p < 0.05).