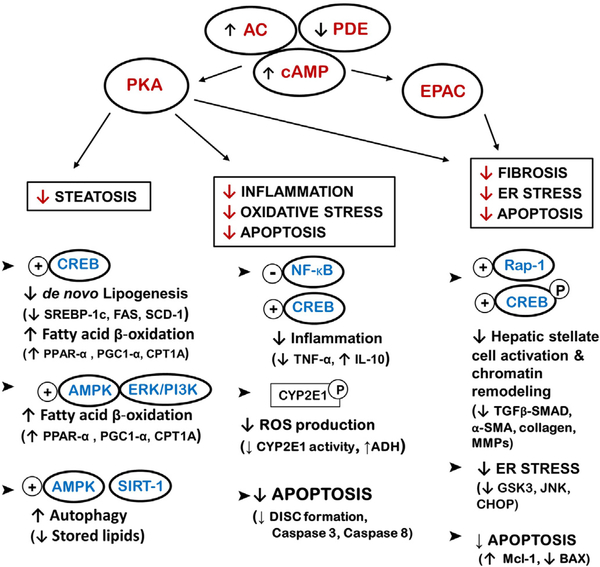
Fig. 2.
A schematic diagram cataloguing cAMP/PKA/EPAC-mediators and targets in NAFLD, ALD and liver fibrosis. The diagram also demonstrates pathways modulated by cAMP/PKA/EPAC activation and the overall effects in the liver such as lipid metabolism, inflammation, oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, apoptosis and fibogenesis. Some of the mediators that have been shown to be key for the beneficial effects of increasing/restoring cAMP in liver disease are mentioned in brackets. AC-adenylate cyclase, PDE-phosphodiesterase, cAMP - cyclic adenosine monophosphate, PKA - protein kinase A, EPAC- exchange protein activated by cAMP, CREB - cAMP response element-binding protein, AMPK - AMP-activated protein kinase, ERK/PI3K extracellular signal-regulated kinases/PI 3-kinases, SREBP-1c - sterol regulatory element-binding protein −1c, FAS - fatty acid synthase, SCD-1 - stearoyl-CoA desaturase, PGC-1α - peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha, PPAR-α - peroxisome-proliferator activator receptor alpha, CPT1A - carnitine palmitoyl transferase 1A, NF-κB - nuclear factor-kappa B, TNFα - tumor necrosis factor alpha, IL-10 - interleukin 10, ROS - reactive oxygen species, ADH - alcohol dehydrogenase, DISC - death-inducing signaling complex, ER - endoplasmic reticulum, GSK3 - glycogen synthase kinase 3, JNK c-Jun N-terminal kinases, CHOP - C/EBP homologous protein, TGF-β - transforming growth factor beta, α-SMA - alpha smooth muscle actin, MMPs - matrix metalloproteinases.