Fig 6. The crystal structure of the complement inhibitory domain of BBK32.
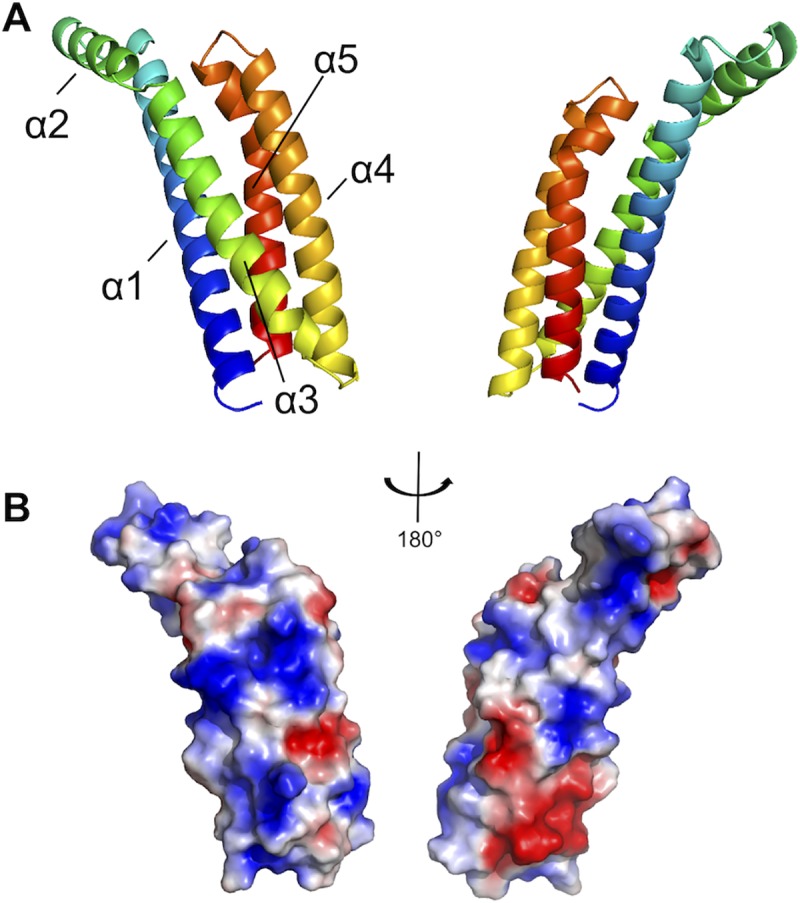
A) The structure of BBK32(206–348) solved at 1.7Å resolution (PDB: 6N1L). A ribbon diagram representation using a spectrum-based coloration scheme of BBK32(206–348) where the N-terminal region of the protein is colored in blue and the C-terminus in red. The structure is shown turned 180° about the y-axis. BBK32(206–348) is characterized by a helical bundle fold where helices 1, 3, 4, and 5 form a core four-helix bundle motif and helix 2 extends away from the core at ~120° relative to helix 3. B) BBK32 is drawn in a surface representation in the same orientations as depicted in panel A. The Adaptive Poisson-Boltzmann Solver as implemented in Pymol was used to calculate the electrostatic potential of the molecular surface. The color scheme represents a gradient of electrostatic potential where regions of negative (red) and positive (blue) are contoured at ± 2 kbT/e where kb is Boltzmann’s constant = 1.3806 x 10−23 J K-1, T is temperature in K, and e is the charge of an electron = 1.6022 x10-19 C.
