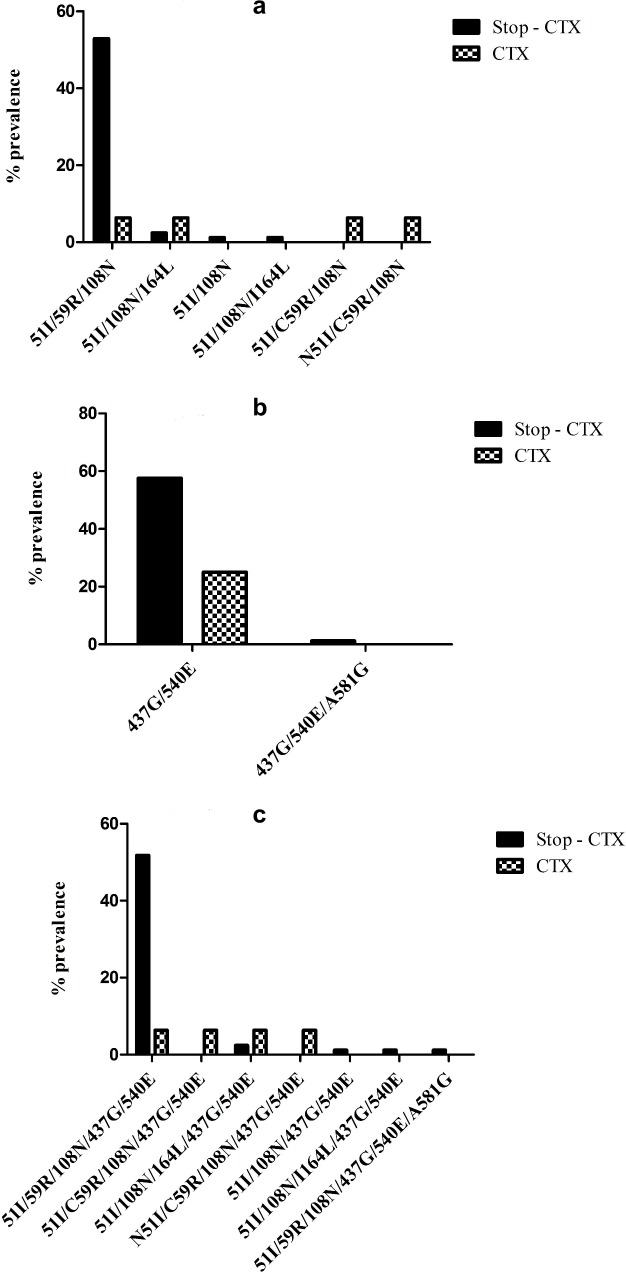
Fig 1. Prevalence of haplotype mutations in pfdhfr and pfdhps genes in subjects continuing with cotrimoxazole prophylaxis therapy (CTX) and those who stopped CTX therapy (STOP CTX).
The prevalence was based on the total number of P. falciparum positive samples in each arm. The statistical difference in parasite prevalence between the two arms was determined. A) Haplotype mutations (51I, 59R, 108N and 164L) in pfdhfr gene; B) haplotype mutations (437G, 540E and 581G) in pfdhps gene and; C) haplotype mutations present in both genes. There were statistical significant differences between the STOP CTX and CTX arms in the pfdhfr gene haplotype 51I/59R/ 108N (P = 0.0006), in pfdhps gene haplotype 437G/540E (P = 0.027) and in both genes haplotype 51I/59R/108N/437G/540E (P = 0.0007).