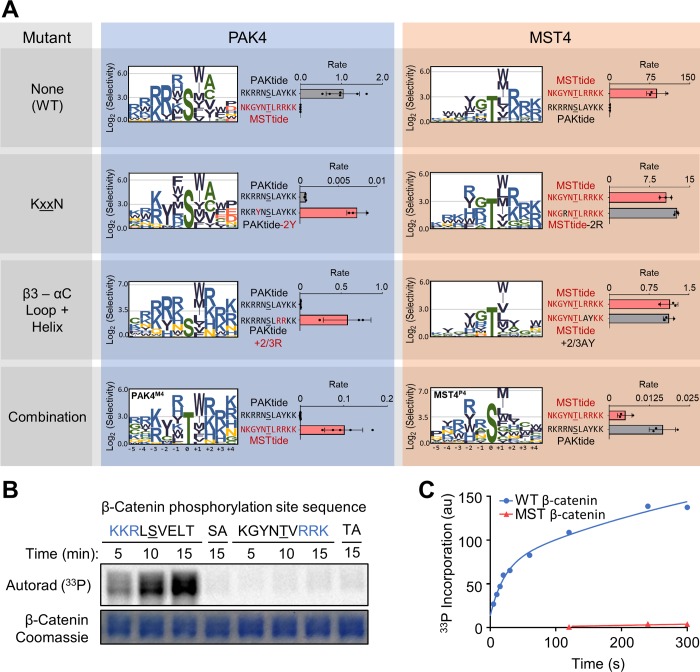
Fig 4. Mutation of specificity-determining residues exchanges substrate specificity between PAK4 and MST4.
Mutants harbor residues found at the indicated positions in the other kinase as described in the main text. The combination mutants (PAK4M4 and MST4P4) include KxxN, DFG+1 and β3–αC loop region mutants (and S445N for PAK4M4). (A) Logos show positively selected residues from PSPA analysis of the indicated mutant kinases. Data were processed and visualized as in Fig 1. Bar graphs show peptide kinase assays with the indicated pairs of peptide substrates (n = 3, error bars indicate SD, rate units are nM/min/nM kinase). (B) Autoradiograph shows in vitro phosphorylation of full-length β-catenin variants with the indicated sequences surrounding Ser675 by WT PAK4. SA and TA are the corresponding S675A or T675A mutants. All β-catenin constructs included two additional mutations to remove minor sites of phosphorylation (S552A/T556A). (C) The graph shows the level of WT PAK4 phosphorylation of β-catenin variants used in (B) over time under pre-steady–state conditions. Numerical data for (A) and (C) are in S2 Data. MST, Mammalian sterile 20 kinase; PAK, p21-activated kinase; PSPA, positional scanning peptide array; WT, wild type.