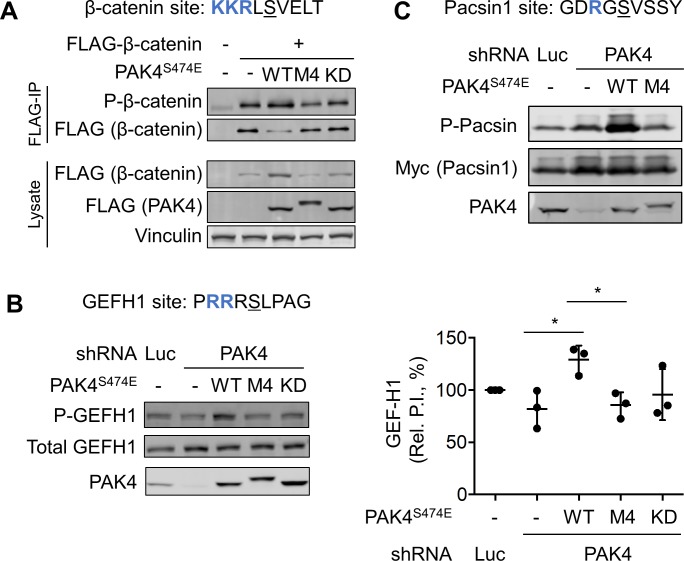
Fig 6. Catalytic site interactions are required for PAK4 to target protein substrates in cells.
(A) HEK293A cells were co-transfected with plasmids expressing FLAG-epitope–tagged β-catenin and PAK4S474E with the additional mutations as indicated. Following FLAG immunoprecipitation from cell lysates, equal amounts of purified β-catenin were subjected to immunoblotting to detect phosphorylation at Ser675. (B) Panc1 cells expressing a doxycycline-inducible shRNA directed to PAK4 or a nontargeting control shRNA were transfected with plasmids expressing the indicated forms of PAK4S474E. Phosphorylation of endogenous GEF-H1 at Ser886 was assessed by immunoblotting with a phosphospecific antibody. The phosphorylation index (ratio of phospho-GEF-H1 to total GEF-H1) was quantified and normalized to the empty vector control (n = 3, error bars indicate SD). Empty vector, PAK4S474E, and PAK4M4/S474E signals were compared with unpaired t tests (*p < 0.05). Numerical data are provided in S2 Data. (C) The Panc1 cell lines used in (B) were co-transfected with plasmids expressing Myc-epitope–tagged Pacsin1 and the indicated PAK4S474E mutants, and Pacsin1 phosphorylation at Ser346 was analyzed by immunoblotting. GEF-H1, Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor H1; HEK, human embryonic kidney; IP, immunoprecipitation; KD, kinase-inactive mutant; Pacsin1, Protein kinase C and casein kinase substrate in neurons protein 1; PAK, p21-activated kinase; P.I., phosphorylation index; P-, phospho-; shRNA, short hairpin RNA; WT, wild type.