Figure 1. Validation of an in vitro, single well, fluorescence-based coupled assay that measures protein acyl transferase catalyzed autopalmitoylation activity.
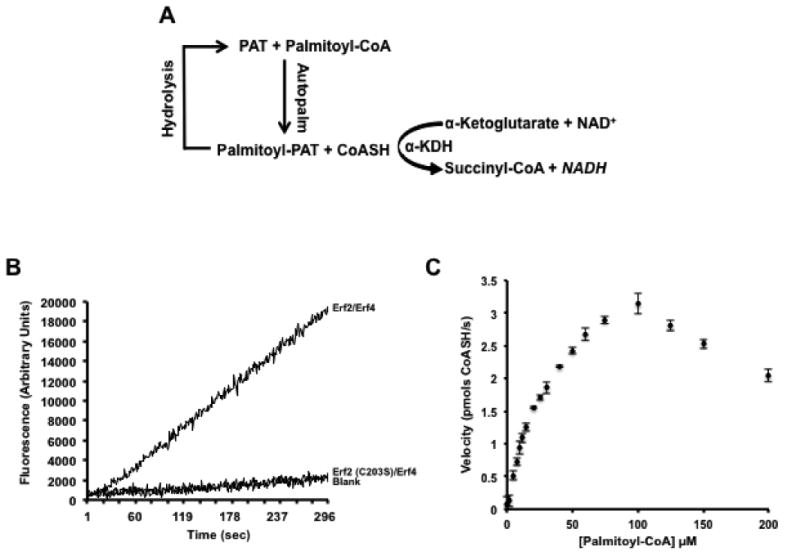
(A) Schematic of the coupled assay reaction. (B) Production of CoASH is dependent on active Erf2-Erf4 complexes. The reaction was performed as described in the Experimental Procedures using 2 μg wild type Erf2-Erf4 complexes, catalytically dead Erf2 (C203S)-Erf4 complexes or boiled Erf2-Erf4 complexes (Blank). Fluorescence was recorded continuously (ex. 340 nm/ em. 460 nm) for 5 min at 30°C. (C) Graphic representation of reaction rates using varying concentrations of palmitoyl-CoA substrate. Reactions were performed in quadruplicate and repeated three times (n=3) at 30°C with intermittent shaking. The fluorescence values (ex. 340 nm/ em. 460 nm) were recorded at 1 min intervals for 10 min. The data was analyzed and fitted using the Michaelis-Menten algorithm of Prism 6 (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA). The data was corroborated using the Direct Linear Plot method [52, 53]. The amount of CoASH produced was based on a standard curve using known concentrations of CoASH and expressed as pmols/s +/- SD.
