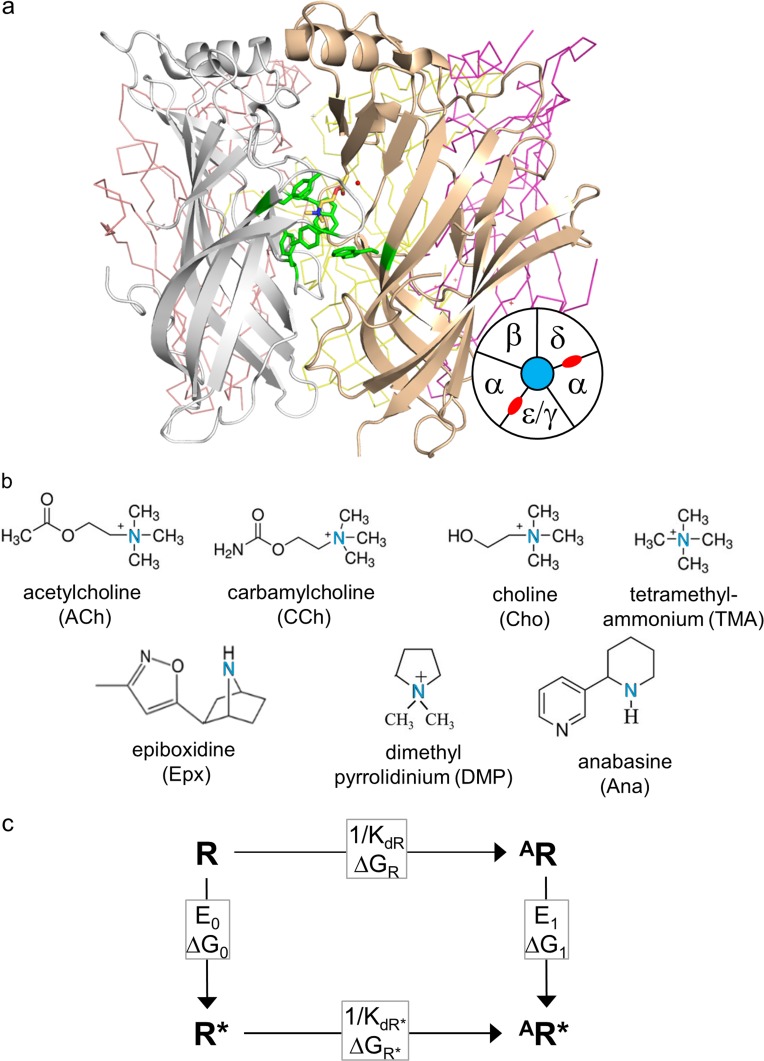
Figure 1.
Sites, agonists, and cycle. (a) Ligand binding sites. Side view of an acetylcholine binding protein, homologous to the AChR extracellular domain (PDB ID: 3WIP; Olsen et al., 2014). Sites are at subunit interfaces. The agonist (ACh, yellow) is surrounded by a cluster of aromatic residues (green). In endplate AChRs, the principal subunit (white) is α and the complementary subunit is δ, ε (adult), or γ (fetal). Bottom right: Top-view schematic of endplate AChR subunits (neurotransmitter binding sites, red). (b) Agonist structures. The principal nitrogen is blue. (c) Cyclic activation scheme for a receptor having one functional binding site. Horizontal, agonist binding and vertical, receptor activation (“gating”). R, resting state (low affinity and closed channel); R*, active state (high affinity and open channel); A, agonist. Boxed, equilibrium constants and free-energy changes (in the direction of the arrow). KdR and KdR*, resting and active equilibrium dissociation constants; E0 and E1, un- and mono-liganded gating equilibrium constants.