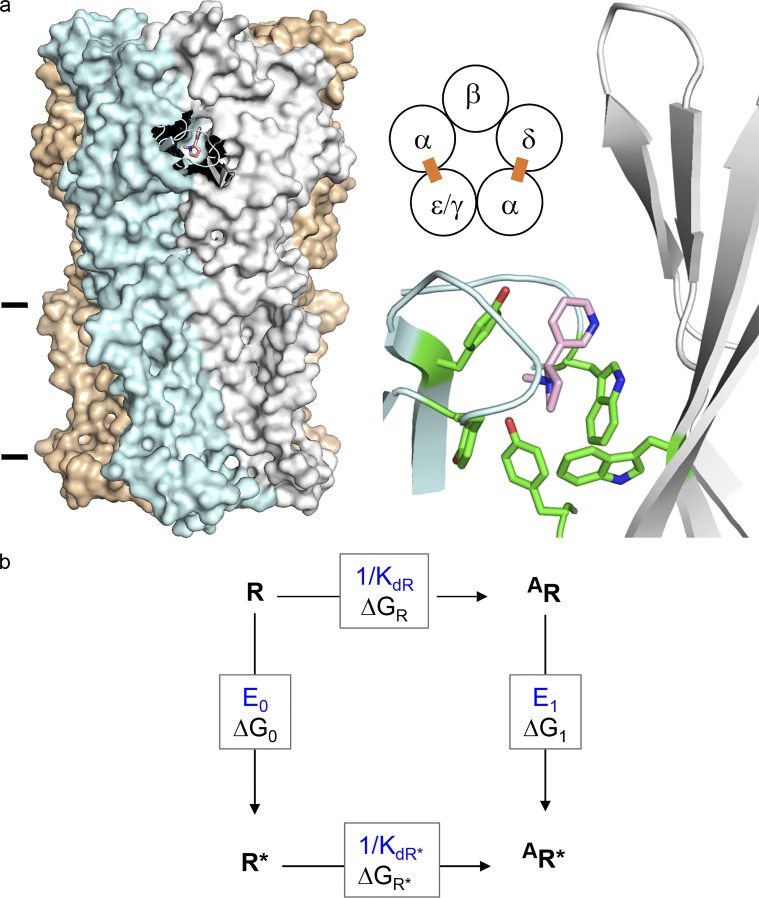
Figure 1.
AChR structure and function. (a) Neurotransmitter binding sites. Left, each site is at a subunit interface (PDB ID 5KXI; Morales-Perez et al., 2016). α-subunit (blue), nicotine (pink), and lines mark approximately the membrane. Middle, each endplate AChR has two neurotransmitter binding sites (ε is adult and γ is fetal). Right, at each site a cluster of aromatic amino acids surrounds the agonist. (b) A cyclic scheme describes receptor operation. Horizontal, agonist binding; vertical, receptor gating. R, resting state (low affinity and closed channel); R*, active state (high affinity and open channel); A, agonist. ΔGR and ΔGR*, binding free energy changes (in direction of arrow) to R and R*; ΔG0 and ΔG1, gating free energy changes with zero and one bound agonist. Corresponding equilibrium constants, blue. Agonists are ligands that bind more strongly to R*.