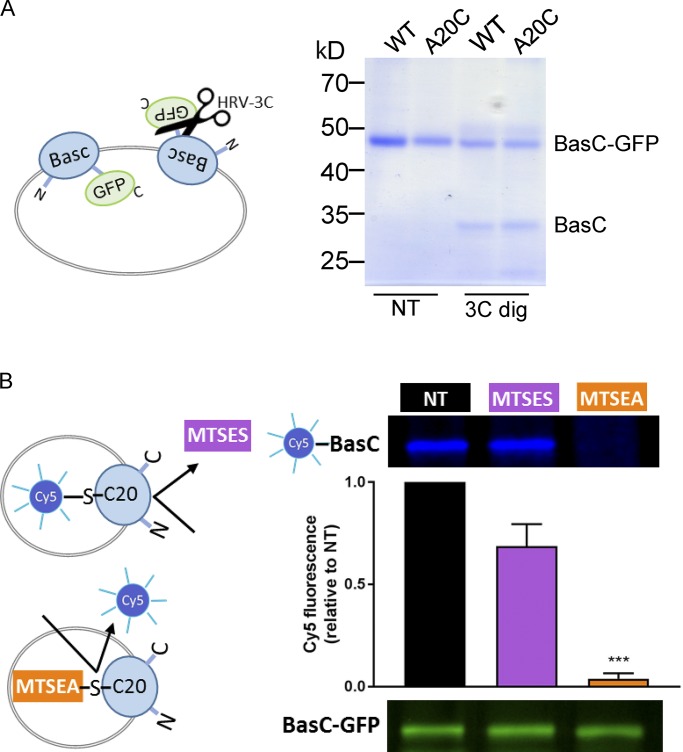
Figure 8.
Vectorial modification of BasC A20C mutant by MTSES from the extracellular side. (A) Random incorporation of the BasC-GFP protein in PLs. BasC-GFP-PLs for wild-type and A20C mutant were treated with HRV-3C protease (3C dig) for 2 h at 4°C. The protease site is accessible in the inside-out BasC-GFP–inserted molecules, resulting in GFP cleavage. Protease-treated PLs were then mixed with loading sample buffer and analyzed in a 10% polyacrylamide gel. As a result, approximately half of the wild-type and mutant proteins were inserted right-side-out when reconstituted in E. coli polar lipid liposomes. (B) MTSEA but not MTSES pretreatment of BasC-A20C-GFP-PLs protected inside-out molecules from Cy5-maleimide dyeing. BasC-A20C-GFP-PLs were digested with HRV-3C protease for 2 h at 4°C to remove GFP from the inside-out BasC-A20C molecules. Then, either MTSES (1 mM; 15 min) or MTSEA (5 mM; 30 min) pretreatment was performed before BasC-A20C labeling with the membrane-permeable reagent Cy5-maleimide (1 mM; overnight). Finally, samples were mixed with loading sample buffer and analyzed in a 10% polyacrylamide gel. In-gel fluorescence at 600 nm (GFP) and 700 nm (Cy5) is shown. The graph represents quantification of Cy5 fluorescence in BasC-A20C normalized by GFP fluorescence in BasC-A20C-GFP and relative to aliquots nontreated with MTSES or MTSES in each experiment (NT). Data (mean ± SEM) are from four independent experiments. Student’s t test for paired data was used for statistical comparison between NT and MTSES (no significant differences) or MTSEA (***, P ≤ 0.001) treatments.