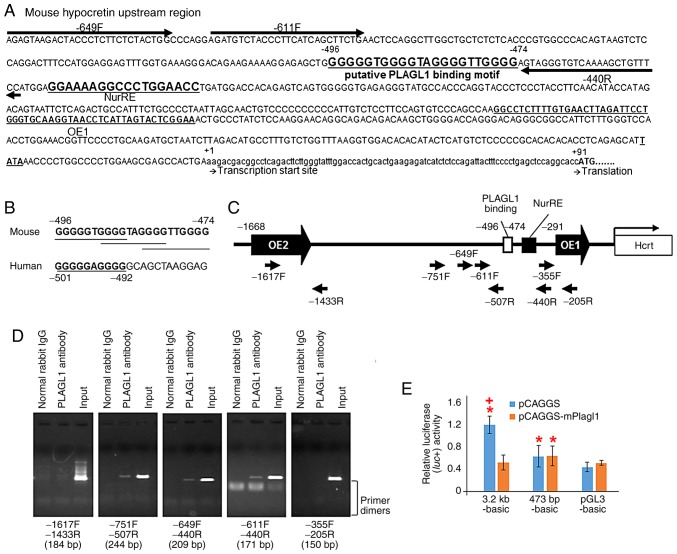
Figure 4.
Schematic representation of the murine prepro-hypocretin gene regulatory region, putative PLAGL1 binding sites in mice and humans, ChIP-PCR and luciferase reporter assay. (A) Sequence of the murine prepro-hypocretin gene regulatory region. Highly conserved region orexin regulatory element 1, which has been previously reported (2,3). The first residues of the transcription start site and the translation start site are marked as +1 and +91, respectively. NurRE (8), the putative PLAGL1 binding site and primers for ChIP-PCR analysis are shown. (B) Putative PLAGL1 binding sites in mouse and human promoter sequences are shown in bold and are underlined. (C) Schematic representation of the murine prepro-hypocretin gene regulatory region, and the position of ChIP-PCR primers. (D) ChIP-PCR analysis of endogenous PLAGL1 binding using ChIP-PCR primers. The length of each PCR product is represented at the bottom of each image. (E) Transcriptional activities of the human prepro-hypocretin promoter and murine deletion mutants in NIH3T3 cells. *P<0.05 vs. pGL3-basic with pCAGGS vector. +P<0.05 vs. each reporter with pCAGGS-mPlagl1. ChIP, chromatin immunoprecipitation; IgG, immunoglobulin G; NurRE, nuclear receptor response element; PLAGL1, pleomorphic adenoma gene-like 1; PCR, polymerase chain reaction.