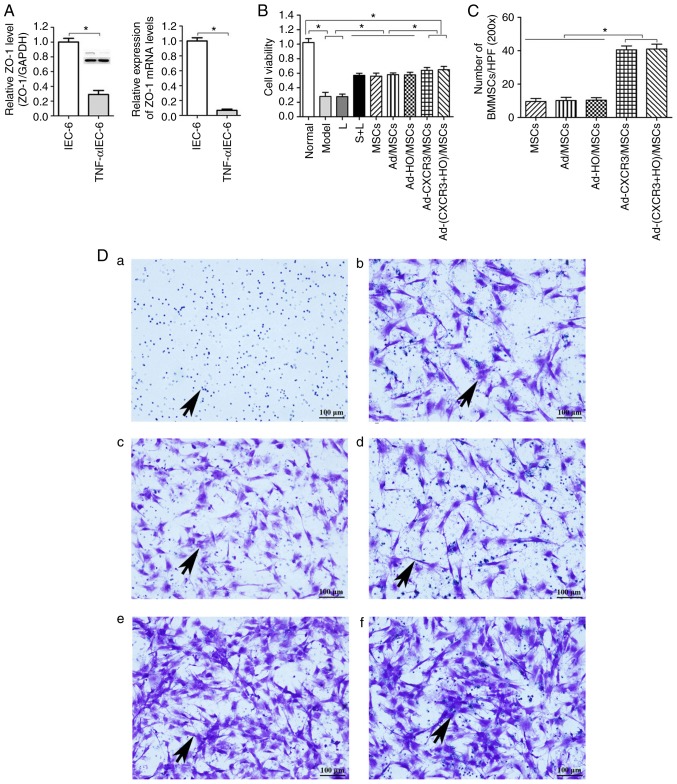
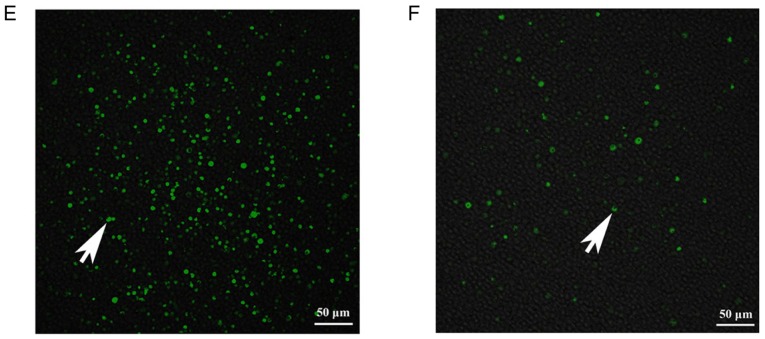
Figure 2.
Validation of the TNF-α/IEC-6 model, IEC-6 cell viability and BMMSC chemotaxis. (A) Protein and mRNA content of ZO-1 in IEC-6 cells and TNF-α/IEC-6. (B) IEC-6 viability in each of the groups was detected. (C) BMMSC migration; the number of migrated BMMSCs in the Ad-CXCR3/MSCs + L and Ad-(CXCR3 + HO)/MSCs + L groups were all higher than in the other groups. (D) Migrated BMMSCs across Transwell membranes (indicated by black arrows): (a) L group, (b) MSC + L group, (c) Ad/MSCs + L group, (d) Ad-HO/MSCs + L group, (e) Ad-CXCR3/MSCs + L group, and (f) Ad-(CXCR3 + HO)/MSCs + L (scale bar, 100 µm). (E) A large number of CXCR3-modified BMMSCs migrated together at 1 h, whereas a (F) small number of BMMSCs without the CXCR3 gene modified began to migrate at 4 h (indicated by white arrows; scale bar, 50 µm). *P<0.05. IEC-6, intestinal epithelial crypt cell line-6; ZO-1, zonula occludens-1; TNF-α; tumor necrosis factor-α; BMMSCs, bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells; Ad, adenovirus; CXCR3, CXC-chemokine receptor CXCR3; HO-1, heme oxygenase-1; L, lymphocytes; S, S203580.