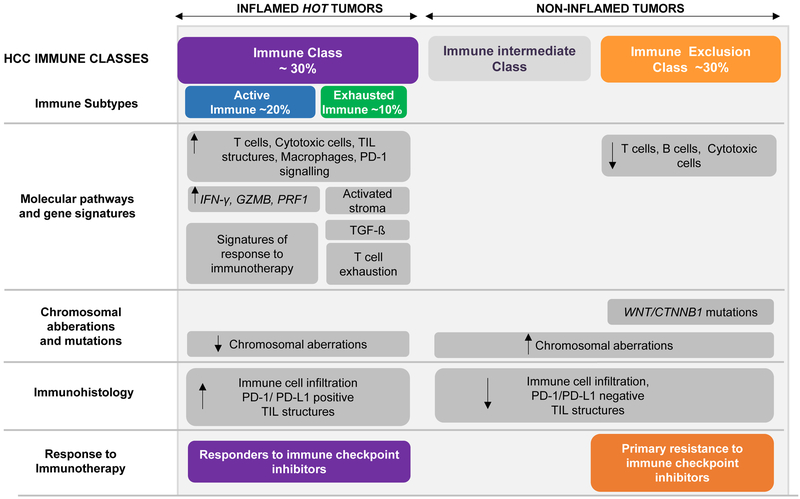
FIGURE 1.
Molecular classification of HCC based upon immune status. Around 30% of HCCs belong to the ‘Immune class’, with high levels of immune cell infiltration, expression of PD-1 and/or programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (PD- L1), activation of IFNγ signaling, and markers of cytolytic activity (such as granzyme B and perforin 1). This HCC tumors are more likely to respond to immune checkpoint inhibitors. On the other hand, the ‘Immune Exclusion class’ accounting for ~30% of HCCs, is characterized by T cell exclusion from the TME and CTNNB1 mutations. Tumors classified within the HCC Exclusion class would represent those with innate resistance to anti-PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors. Non-inflamed tumors with wild-type CTNNB1 and intermediate levels of immune infiltration (the so called ‘Immune intermediate class’) needs to be further characterized to be able to anticipate the response that these patients would have when treated with immunotherapies. Figure partly modified from Llovet et al. (2).