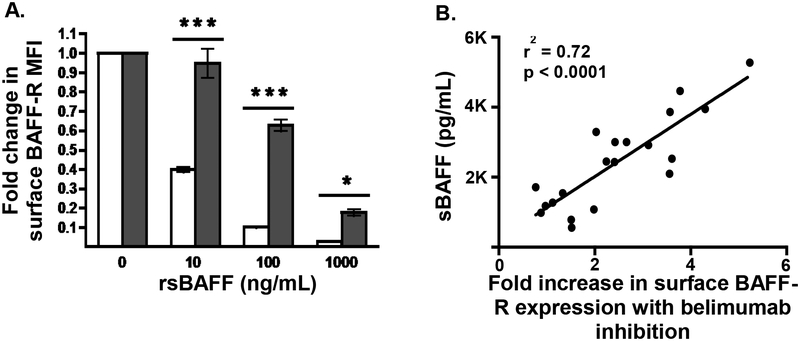
Figure 2. Effect of sBAFF on surface BAFF-R expression.
A. Healthy donor isolated CD19+ B cells (n=5) were incubated overnight in complete media (10% FCS in 1640 RPMI) at 37°C with stated concentrations of recombinant soluble BAFF and surface expression of BAFF-R was measured by flow cytometry and compared to complete media alone (white bars). To measure the effect of receptor occupancy on flow cytometry antibody binding caused by rsBAFF binding to BAFF-R, the same concentrations of rsBAFF were incubated with the same healthy donor CD19+ B cells at 4°C (gray bars). The bars represent means ± SEM compared using paired T test. MFI, mean fluorescence intensity. *P < .05 ***P < .001, B. Plasma from patients post-HCT down-modulates surface expression of BAFF-R on pre-B ALL 697 cells. 697 cells were incubated with a 1:1 mix of complete media and patient plasma (n=20) with or without belimumab (10 ug/mL) overnight and surface expression of BAFF-R was measured by flow cytometry. The MFI was compared between both conditions for each sample and expressed as fold increase in BAFF-R due to sBAFF inhibition by belimumab. This was then correlated to soluble BAFF levels.