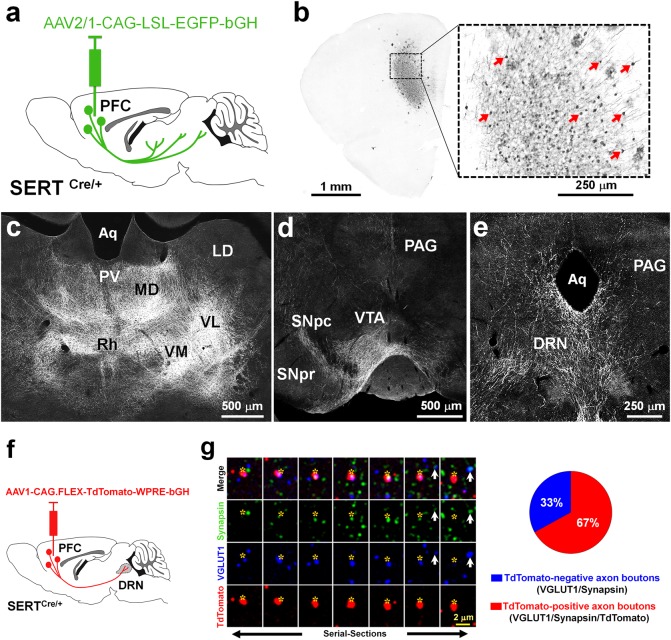
Fig. 2.
Subcortical brain targets of PFC-SERT+ neurons and their large contribution to the PFC-to-DRN synaptic circuit. a Schematic illustration of the injection site in the PFC. The AAV2/1-CAG-LSL-EGFP-bGH virus was used for conditional anterograde tracing in SERTCre/+ mice. Injection was done at P4–5 and histology 3 weeks after. b Effective recombination is visible in PFC neurons that express EGFP (indicated by arrows). c-e Main brain targets of PFC-SERT+ neuron axons: c Thalamic nuclei including the paraventricular (PV), mediodorsal (MD), rhomboid (Rh), ventromedial (VM), and ventrolateral (VL) nuclei; (d) the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc) and ventral tegmental area (VTA); (e) the dorsal raphe nucleus (DRN) and periaqueductal gray (PAG). Laterodorsal nucleus (LD), aqueduct (Aq), substantia nigra pars reticulata (SNpr). f AAV1-CAG.FLEX-TdTomato-WPRE-bGH was bilaterally injected in the PFC of P4-P5 SERTCre/+ mice used for the array tomographic anterograde tracing analysis in the DRN. g Array tomography image of seven serial-ultrathin 70-nm sections immunolabeled against synapsin (green), VGLUT1 (blue), and TdTomato (red), after anterograde viral tracing from the PFC. Asterisks indicate the same PFC TdTomato-positive axon terminal across the multiple serial sections often colabeled for VGLUT1 and synapsin. The arrow indicates a cortical axon bouton negative for TdTomato. The pie chart shows the percentages of cortical axon boutons present in the DRN that exclusively originated from PFC-SERT neurons (67 ± 8 %, red) in comparison with those arising from other cortical neurons (33 ± 8 %, blue)