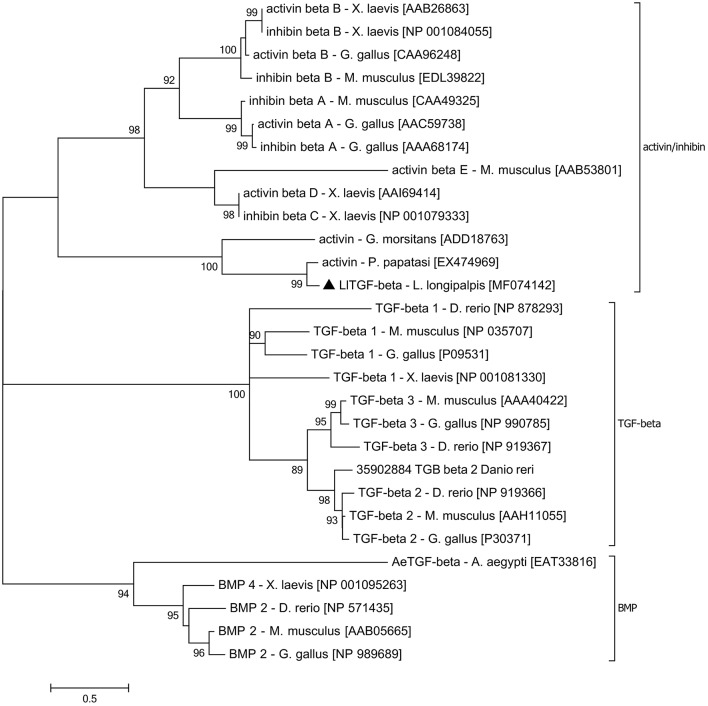
Figure 1.
LlTGF-β phylogenetic tree. The LlTGF-β deduced amino acid sequence was aligned with other TGF-β sequences from the insect vectors Aedes aegypti, Glossina morsitans, Phlebotomus papatasi, and the vertebrates Danio rerio, Gallus gallus, Mus musculus, Xenopus laevis. The evolutionary history was inferred using MEGA 6.06 software with Maximum Likelihood method based on the JTT matrix-based model. Evolutionary rate differences among sites [5 categories (+G, parameter = 3.2942)] were modeled by discrete Gamma distribution. The rate variation model allowed for some sites to be evolutionarily invariable ([+I], 2.1884% sites). Positions with gaps and missing data were eliminated. The TGF-β subfamily groups are indicated on the right side of the phylogram. Each sequence is labeled with species name followed by GenBank accession number. Branch length represents numbers of substitutions per site. Numbers on the tree nodes indicate bootstrap values higher than 85% (500 replicates).